A recent study from Heidelberg University Hospital and the Medical Faculty of Heidelberg University has revealed that oral diseases, including tooth decay (caries), periodontitis (gum disease), and tooth loss, cost the global economy approximately $710 billion every year. This staggering figure highlights the immense financial burden of dental health issues on both individuals and society.
Published in the Journal of Dental Research, the study draws attention to the critical role that oral health plays in public health and economics. It was included in the World Health Organization’s (WHO) first-ever Global Oral Health Status Report and its accompanying Global Oral Health Action Plan for 2023–2030.
A Global Economic Burden
The study, led by Professor Dr. Dr. Stefan Listl, Head of the Oral Health Section at the Heidelberg Institute of Global Health, analyzed data from 194 countries to estimate the global economic cost of dental diseases. The total cost for 2019 was found to be approximately $710 billion (or €640 billion), divided into two categories: direct costs (around $387 billion or €341 billion) and indirect costs, primarily from lost productivity, totaling about $323 billion (or €299 billion).
The study’s findings show that tooth loss and periodontitis account for most of the productivity losses worldwide. These two conditions alone were responsible for nearly 75% of the total indirect costs.
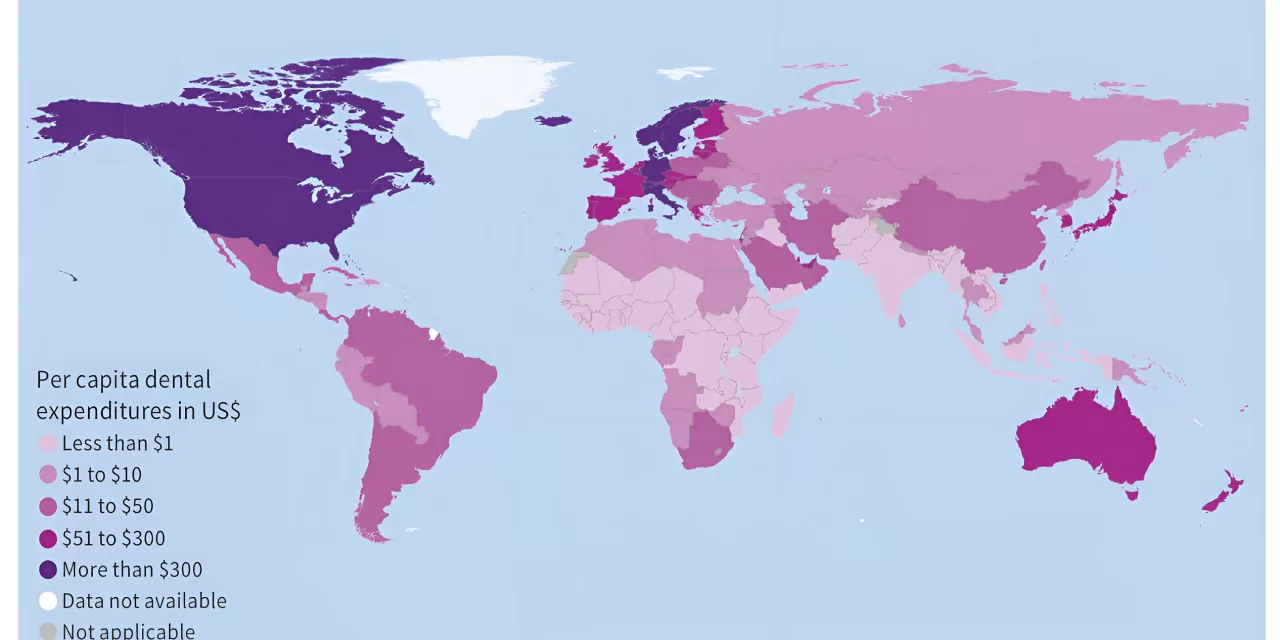
In Germany, for instance, the direct expenditure on dental care in 2019 was $30.9 billion (€27.8 billion), or $372 (€334) per capita. The indirect costs, including productivity losses, amounted to $19.4 billion (€17.5 billion), with each person losing approximately $232 (€208) in productivity due to oral health issues.
Disparities Between Countries
The study also reveals a stark contrast between low- and high-income countries in terms of dental care spending. In low-income nations, the average per capita expenditure on dental care was just $0.52 (€0.47) annually, compared to $260 (€233) in high-income countries. In Germany, the per capita expenditure was significantly higher at $372 (€334).
Professor Listl pointed out that while Germany has a relatively well-established dental care system, there are still challenges to address, such as a growing shortage of dental practices in rural areas and ensuring continuous dental care for vulnerable populations, including those in need of long-term care.
The Need for Preventative Measures
The economic impact of oral diseases underscores the importance of preventative measures, as many dental conditions are preventable or can be treated early. According to the WHO, more than 3.5 billion people globally suffer from some form of oral disease, with dental conditions being among the most common chronic health issues worldwide. The WHO and Listl both emphasize the need for cost-effective oral health interventions and increased access to affordable dental care.
In particular, reducing sugar consumption and improving access to preventive dental services could alleviate the economic burden of oral diseases. As Listl’s study highlights, there is a pressing need for governments to adopt prevention-oriented oral health policies and develop plans for a more equitable distribution of oral healthcare resources.
WHO’s Focus on Oral Health
The WHO’s recent efforts, including its Resolution on Oral Health and the Global Oral Health Action Plan, aim to raise awareness of the economic and health impacts of oral diseases. Dr. Benoit Varenne, Officer of the WHO Oral Health Program, emphasized the significance of this research in shaping future global oral health policies and prioritizing cost-effective solutions.
The findings of this study will be discussed in greater detail at the upcoming WHO global oral health meeting in Bangkok, Thailand, from November 26 to 29. Professor Listl will also be attending the event as a co-coordinator for a side event titled “Investing More, Investing Better: Using Economics to Help Shape Oral Health Policy.”
The study’s comprehensive analysis of the economic impact of oral diseases is an important step towards advocating for more sustainable and equitable oral health systems globally.
Source: M. Jevdjevic et al, Global, Regional, and Country-Level Economic Impacts of Oral Conditions in 2019, Journal of Dental Research (2024). DOI: 10.1177/00220345241281698