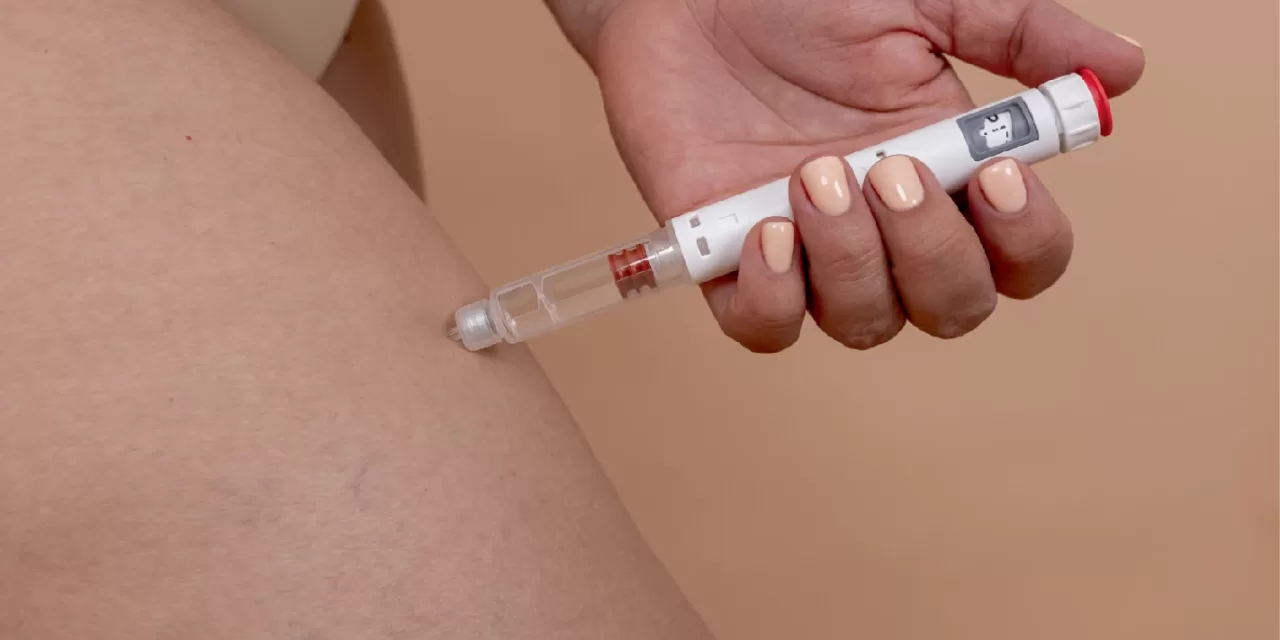
Approximately 15.5 million Americans have experienced or are currently undergoing treatment with injectable medications for diabetes and weight loss, known as GLP-1 receptor agonists. Among the most well-known brands are Ozempic, Wegovy, Mounjaro, and Zepbound. With obesity rates on the rise, eligibility expanding, and an increasing curiosity about their benefits, more individuals are exploring the potential advantages of these medications.
What are GLP-1 Medications?
GLP-1 medications, such as semaglutide (Ozempic) and tirzepatide (Mounjaro), have revolutionized the treatment of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Semaglutide, first marketed as Ozempic, gained immense popularity after trial data highlighted its superior potency compared to other GLP-1 medications, such as dulaglutide (Trulicity). Social media further amplified the success of Ozempic, leading to wider recognition and use.
Tirzepatide, the more potent relative, has also gained traction as a treatment for both diabetes and weight loss. Initially developed for type 2 diabetes, these medications have gained traction due to their unexpected weight loss benefits. Following this trend, the makers of Ozempic introduced Wegovy for weight loss, while Mounjaro’s weight-loss counterpart, Zepbound, was developed to address the same needs.
Dr. Andrew Tenpas, PharmD, RPh, a clinical assistant professor at Texas A&M University and a healthcare provider at a South Texas VA clinic, has seen firsthand the life-changing impact of GLP-1 medications. “I have some veterans who have lost 70 to 100 pounds, and it’s completely changed their entire quality of life,” Tenpas remarked. “Not only does it improve blood sugar control, but it also positively affects blood pressure, cholesterol, and mobility.”
How Do GLP-1 Medications Work?
GLP-1 receptor agonists mimic a naturally occurring hormone released in the body after eating, known as GLP-1. This hormone plays a key role in insulin secretion, blood sugar regulation, and appetite control. In individuals with diabetes or obesity, the body either releases insufficient GLP-1 or the hormone doesn’t work as effectively.
These medications, such as Ozempic, help to supplement GLP-1, aiding in blood sugar regulation and appetite control. Newer GLP-1 drugs, like tirzepatide, combine GLP-1 with glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), a hormone that further enhances the medication’s efficacy, especially in promoting weight loss.
The result is two-fold: individuals experience reduced appetite, feel full longer, and benefit from better blood sugar control. Research suggests that GLP-1 medications also improve cholesterol and blood pressure levels, making them highly beneficial for individuals struggling with metabolic conditions.
Is GLP-1 Medication Right for You?
GLP-1 medications are not a quick-fix solution, according to Dr. Tenpas. “These medications are tools, not magic solutions. They’re meant to help reshape your relationship with food and portion sizes, giving you a head start with weight loss so you can focus on adopting healthier habits like exercise,” Tenpas explained.
For many patients, long-term use may not be necessary once they have reached their weight loss goals and embraced sustainable lifestyle changes. If used responsibly, these medications are considered safe for long-term use. However, patients may experience short-term side effects such as nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea, particularly at higher doses or when combined with certain foods.
GLP-1 medications may not be suitable for everyone. Pregnant women, individuals with specific gastrointestinal conditions like gastroparesis or significant kidney disease, and those taking certain medications like glipizide or insulin, should consult their medical provider before using GLP-1 drugs.
The Future of GLP-1 Medications
The future of GLP-1 medications looks promising, with research and trials ongoing to further refine these treatments. At least 27 new GLP-1 drugs are currently in development, with some combining multiple hormones for even greater efficacy. Early trial data suggests that the next generation of GLP-1 drugs may provide even more substantial weight loss benefits.
One exciting development is the prospect of triple-hormone receptor agonists, combining GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors. Early studies published in the New England Journal of Medicine suggest that these medications could provide enhanced outcomes compared to current treatments, potentially ushering in a new era of diabetes and weight loss management.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is provided for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting or changing any medication. GLP-1 medications may not be suitable for everyone and may cause side effects or interact with other medications.