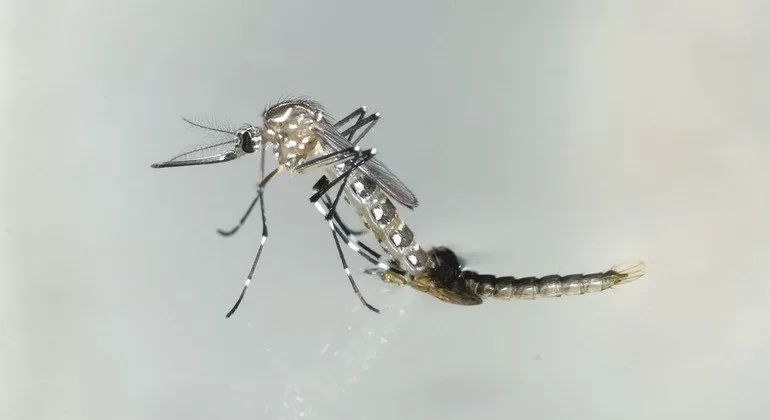
Pune, India – In the wake of recent Zika virus infections affecting five individuals in Pune, health experts have highlighted that the virus is predominantly asymptomatic but can present symptoms akin to dengue fever. The insights were shared during a health advisory on Monday.
Zika Virus Disease (ZVD) is transmitted through Aedes mosquitoes, the same vector responsible for dengue, chikungunya, and yellow fever. These mosquitoes are primarily active during the day. ZVD is typically mild to moderate in severity for adults and generally does not necessitate specific treatment.
Common Symptoms and Asymptomatic Nature
“About 80 percent of Zika virus cases are estimated to be asymptomatic, although this figure’s precision is affected by variable data quality,” said Dr. Suruchi Mandrekar, Consultant in Internal Medicine at Manipal Hospital, Pune, in an interview with IANS.
Symptomatic cases, albeit rare, can mimic dengue fever symptoms, including mild fever, red eyes, joint pain, headache, and a maculopapular rash, Dr. Mandrekar noted.
Factors Contributing to Zika Virus Spread
Dr. Digvijay Adke, Consultant and In-charge of the Emergency Department at DPU Super Specialty Hospital, Pune, explained the rise in Zika virus cases. “The increase is primarily due to sudden weather changes, clogged drains, water accumulation, and poor personal hygiene practices.”
Concerns for Pregnant Women and Severe Complications
Zika virus infection is particularly concerning during pregnancy, as it can lead to microcephaly and other brain malformations in infants, Dr. Mandrekar emphasized. In adults, it has been associated with Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) and affects Schwann cells, which are crucial for the peripheral nervous system’s functions such as movement, breathing, heartbeat, and digestion.
Prevention and Protective Measures
Preventive measures are crucial, given the absence of a vaccine for Zika virus. “Prevention involves minimizing mosquito bites in affected areas and proper condom use to prevent sexual transmission,” Dr. Mandrekar recommended. Effective strategies include using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, utilizing mosquito nets, and eliminating standing water where mosquitoes breed.
Dr. Adke also stressed the importance of hygiene practices. “Regular hand washing and avoiding food from unhygienic sources, especially undercooked items, are advised. Incorporating nutritious foods like fruits and vegetables in the diet helps bolster the immune system, aiding in the fight against vector-borne diseases.”
The health experts’ advice underscores the significance of community awareness and proactive measures to manage and prevent the spread of Zika virus, safeguarding public health.