March 4, 2025
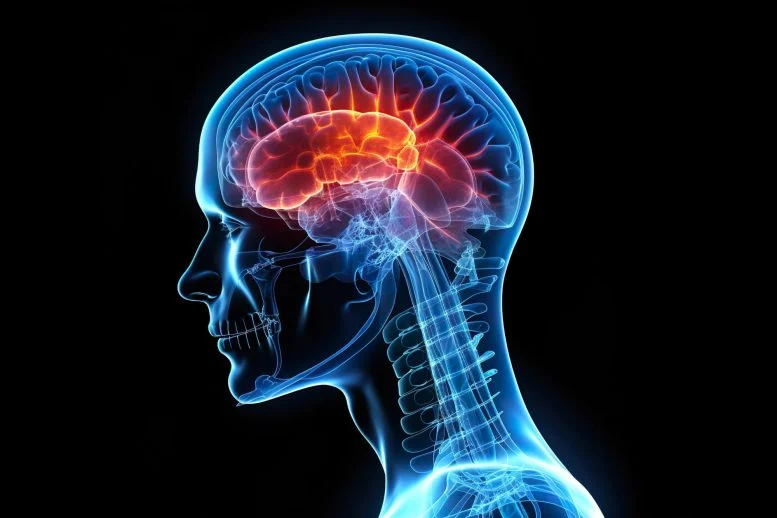
In a significant move to bolster global health initiatives, the World Health Organization (WHO) has officially designated encephalitis as a public health priority. This decision underscores the urgency of addressing the rising incidence and impact of encephalitis worldwide.
Understanding Encephalitis
Encephalitis, an inflammation of the brain, can result from infections or autoimmune responses. Symptoms range from mild flu-like signs to severe neurological impairments, including seizures, memory loss, and in extreme cases, death. The condition poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems and significantly affects the quality of life of those afflicted.
WHO’s Strategic Focus
By elevating encephalitis to a public health priority, the WHO aims to:
- Enhance Surveillance: Implement comprehensive monitoring to accurately assess the global prevalence and trends of encephalitis.
- Improve Diagnostics: Promote the development and accessibility of rapid, accurate diagnostic tools to facilitate timely treatment.
- Advance Treatment Protocols: Support research into effective therapies and standardize care practices to improve patient outcomes.
- Strengthen Prevention Efforts: Encourage vaccination and other preventive measures to reduce the incidence of encephalitis caused by infectious agents.
Global Health Implications
This initiative aligns with the WHO’s broader objectives to combat neurological diseases and enhance global health infrastructure. By prioritizing encephalitis, the WHO seeks to mobilize resources, foster international collaboration, and stimulate research to address the challenges posed by this condition.
Disclaimer: The information presented in this article is based on reports from the World Health Organization and other reputable health sources. For personalized medical advice or more detailed information, please consult healthcare professionals or visit the official WHO website.