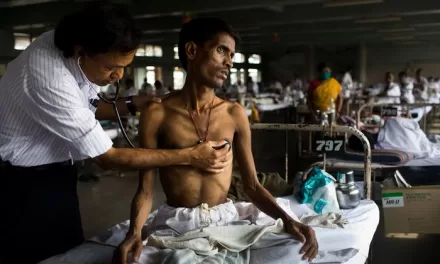
Sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by the body’s extreme response to infection, has emerged as a silent killer in India. While cancer receives significant attention in terms of research, treatment facilities, and awareness campaigns, sepsis remains underdiagnosed and undertreated, leading to a higher death toll.
The Alarming Reality of Sepsis in India
Studies indicate that sepsis accounts for a significant proportion of hospital deaths in India, surpassing fatalities from cancer. Several factors contribute to this high mortality rate:
1. Lack of Awareness and Early Diagnosis
Unlike cancer, which has dedicated screening programs and public awareness initiatives, sepsis remains relatively unknown among the general population. Its symptoms—fever, rapid heart rate, confusion, and breathing difficulties—are often mistaken for other infections, delaying crucial treatment.
2. Inadequate Healthcare Infrastructure
Many hospitals, particularly in rural areas, lack the necessary diagnostic tools and intensive care units (ICUs) to manage sepsis effectively. Timely administration of antibiotics and organ support is critical, but delays in reaching medical facilities often prove fatal.
3. Widespread Antibiotic Resistance
India has one of the highest rates of antibiotic resistance, making infections harder to treat. The unregulated use of antibiotics has led to the development of superbugs that do not respond to conventional treatments, increasing the risk of sepsis-related complications.
4. High Burden of Infections
Poor sanitation, contaminated water, and inadequate infection control measures in hospitals contribute to the spread of bacterial infections, a primary cause of sepsis. Vulnerable groups such as neonates, elderly individuals, and those with weakened immune systems face the greatest risk.
5. Delayed and Inadequate Treatment
In many cases, sepsis is diagnosed too late, by which time multiple organ failure has already set in. Additionally, financial constraints prevent many patients from accessing life-saving interventions such as ventilators and dialysis.
Addressing the Sepsis Crisis
To reduce sepsis-related mortality, India must implement comprehensive public health strategies:
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Just as cancer awareness has improved early detection rates, educating people about sepsis symptoms and the importance of timely medical intervention can save lives.
- Strengthening Healthcare Facilities: Increasing the number of ICUs, improving diagnostic tools, and training medical professionals are crucial for improving sepsis survival rates.
- Regulating Antibiotic Use: Implementing strict policies on antibiotic prescriptions can help prevent drug resistance and improve treatment effectiveness.
- Improving Sanitation and Hygiene: Addressing the root causes of infections through better hygiene practices and vaccination programs can significantly reduce sepsis cases.
Conclusion
Sepsis remains a major but underrecognized health crisis in India. While cancer continues to be a significant concern, sepsis-related deaths are preventable with better awareness, timely medical intervention, and stronger healthcare policies. Addressing this issue should be a public health priority to save thousands of lives every year.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Readers are encouraged to seek professional medical guidance for diagnosis and treatment of any health condition.