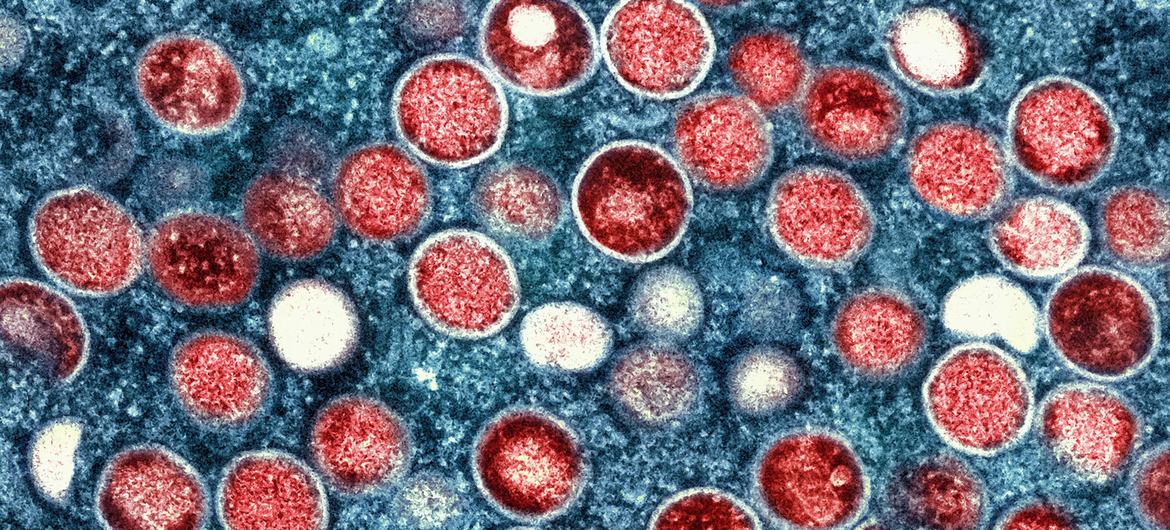
In response to the recent resurgence of mpox in Africa, the World Health Organization (WHO), in collaboration with international partners, has launched an Access and Allocation Mechanism (AAM) to ensure equitable distribution of vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tools. This initiative aims to prioritize populations at the highest risk and optimize the use of limited medical countermeasures, especially in countries experiencing the most severe outbreaks.
The establishment of the AAM follows the declaration of a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC) by WHO Director-General Dr. Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus on August 14, 2024, in light of the significant rise in mpox cases in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and neighboring countries. So far, 15 African nations have reported mpox cases this year. Dr. Tedros emphasized the importance of coordinated global efforts, stating, “Vaccines, therapeutics, and diagnostics are powerful tools for bringing the mpox outbreaks in Africa under control. We urge countries with supplies of these resources to donate, prevent infections, and save lives.”
Access and Allocation Mechanism to Promote Equity
The AAM was developed as part of the interim Medical Countermeasures Network (i-MCM-Net), which unites global partners such as the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention, the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, Gavi, UNICEF, Unitaid, and the European Union’s Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Authority (HERA). This international coalition aims to establish a robust framework for the development, manufacturing, and delivery of vaccines, treatments, and diagnostic tests.
In addition to the mechanism’s establishment, over 3.6 million doses of mpox vaccines have been pledged for distribution. This includes 620,000 doses of the MVA-BN vaccine donated by the European Commission and other countries, as well as 3 million doses of the LC16 vaccine pledged by Japan. These donations mark a significant step forward in combating the growing threat of mpox, particularly in regions facing severe resource shortages.
Guiding Principles of the AAM
The AAM is based on three key principles:
- Preventing Illness and Death: Prioritizing the use of vaccines and other tools for those most at risk to reduce the severity of the outbreak.
- Mitigating Inequity: Ensuring equitable access to medical countermeasures for all at-risk populations, regardless of socio-economic or demographic backgrounds.
- Transparency and Flexibility: Establishing clear communication regarding allocation decisions and adjusting strategies as new data emerges.
The mechanism also emphasizes targeted vaccination campaigns for contacts of confirmed mpox cases and providing countries with point-of-care diagnostic tools, enabling timely detection and care for suspected cases.
Dr. Mike Ryan, Executive Director of WHO’s Health Emergencies Programme, highlighted the importance of a comprehensive approach in controlling the outbreak, saying, “WHO and partners are supporting the DRC and other countries in implementing an integrated approach, including case detection, contact tracing, vaccination, and infection prevention. The AAM will ensure a reliable supply of vaccines and tools to interrupt transmission and reduce suffering.”
Urgency and Collaboration
The sharp increase in mpox cases in Africa underscores the importance of international collaboration to address the crisis. With limited supplies of vaccines and treatments, the WHO and its partners are working to ensure that resources are used where they are needed most.
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the need for a coordinated global response to health crises, and the AAM for mpox aims to apply those lessons to this new challenge. Through ongoing efforts to allocate critical medical resources fairly and efficiently, the WHO and its global partners hope to mitigate the impact of mpox and save lives.
The Access and Allocation Mechanism offers a framework for equitable distribution and international cooperation, essential in managing outbreaks and ensuring global health security.