Situation at a glance
Description of the situation
In many countries of the Northern Hemisphere, trends in acute respiratory infections increase at this time of year. These increases are typically caused by seasonal epidemics of respiratory pathogens such as seasonal influenza, RSV, and other common respiratory viruses, including hMPV, as well as mycoplasma pneumoniae. The co-circulation of multiple respiratory pathogens during the winter season can sometimes cause an increased burden on health care systems treating sick persons.
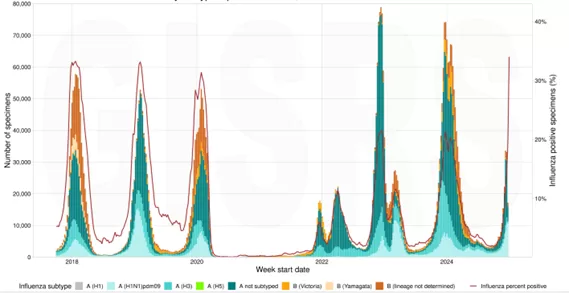
Currently, in some countries in the temperate Northern hemisphere, influenza-like illness (ILI) and/or acute respiratory infection (ARI) rates have increased in recent weeks and are above baseline levels, following usual seasonal trends. Influenza activity is elevated in many countries in Europe, Central America and the Caribbean, Western Africa, Middle Africa, and many countries across Asia, with the predominant seasonal influenza type and subtype varying by location, typical for this time of year, except during most of 2020 and 2021, when there was little influenza activity during the COVID-19 pandemic (Figure 1). SARS-CoV-2 activity as detected in sentinel surveillance and reported to Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System (GISRS), along with wastewater monitoring from the reporting countries, is currently low in countries in the Northern hemisphere following prolonged high level activity during summer months in the Northern hemisphere. Where surveillance data is available, trends in RSV activity are variable by region with downward trends observed in most subregions of the Americas, except in North America where RSV activity has increased, and decreases have been observed in the European region in recent weeks. Some countries conduct routine surveillance and report trends for other commonly circulating respiratory pathogens, such as hMPV, and report such information on a routine basis. Some countries in the Northern hemisphere have reported increased trends, varying by virus, in recent weeks, typical for this time of year.
Figure 1. Virus detections by subtype reported to FluNet, 01 October 2017 to 30 December 2024 from countries in the Northern hemisphere, as of 07 January 2025
Source: (https://worldhealthorg.shinyapps.io/flunetchart/).
There has been international interest in a potential increase of respiratory virus transmission in China, particularly hMPV, including suggestions of hospitals being overwhelmed. China has an established sentinel surveillance system for ILI and severe acute respiratory infections (SARI), including hMPV, and conducts routine virological surveillance for common respiratory pathogens with detailed reports published weekly on the China Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website.[1] Surveillance and laboratory data for hMPV is not available routinely from all countries.
According to the most recent surveillance data on acute respiratory infections shared by the China CDC with data up to 29 December 2024, there has been an upward trend of common acute respiratory infections, including those due to seasonal influenza viruses, RSV and hMPV – as expected for this time of year during the Northern Hemisphere winter. Influenza is currently the most reported cause of respiratory disease, with the highest positivity rate among all monitored pathogens for all age groups except children aged 5-14 years for whom mycoplasma pneumoniae had the highest positivity rate. SARS-CoV-2 activity remains low however with an increase in reported severe COVID-19 cases. The predominant circulating SARS-CoV-2 variant in the country is XDV and its sublineages accounting for 59.1% detection among sequenced samples. ILI activity in China’s northern and southern provinces have been increasing since late 2024, following the previous year’s trends. Current ILI activity in the southern provinces remains below that of the previous two years, while current ILI activity in the northern provinces is similar to levels seen at this time in the previous two years.
China’s reported levels of acute respiratory infections, including hMPV, are within the expected range for the winter season with no unusual outbreak patterns reported. Chinese authorities confirmed that the health care system is not overwhelmed, hospital utilization is currently lower than this time last year, and there have been no emergency declarations or responses triggered. Since the expected seasonal increase was observed, health messages have been provided to the public on how to prevent the spread of respiratory infections and reduce the impact of these diseases.
Public health response
Based on the expected increase in respiratory infections during the winter season, countries, including China, have been providing health messages to the public on how to prevent the spread of respiratory infections and reduce the impact of disease.
WHO risk assessment
In temperate climates, seasonal epidemics of common respiratory pathogens, including influenza, occur often during winter periods. The observed increases in acute respiratory infections and associated pathogen detections in many countries in the Northern hemisphere in recent weeks is expected at this time of year and is not unusual. The co-circulation of respiratory pathogens may pose a burden to health facilities.
WHO advice
WHO recommends that individuals in areas where it is winter take normal precautions to prevent the spread and reduce risks posed by respiratory pathogens, especially to the most vulnerable. People with mild symptoms should stay home to avoid infecting other people and rest. People at high risk or with complicated or severe symptoms should seek medical care as soon as possible. Individuals should also consider wearing a mask in crowded or poorly ventilated spaces, cover coughs and sneezes with a tissue or bent elbow, practice regular handwashing, and get recommended vaccines as per physician and local public health authorities’ advice.[2]
WHO advises Member States to maintain surveillance for respiratory pathogens through an integrated approach, considering country context, priorities, resources and capacities. WHO has published guidance on integrated surveillance here. WHO has also updated guidance on assessing influenza epidemic and pandemic severity, including the impact on healthcare facilities, here.
Based on the current risk assessment, WHO advises against any travel or trade restrictions related to current trends in acute respiratory infections.
Further information
- World Health Organization (WHO). Implementing the integrated sentinel surveillance of influenza and other respiratory viruses of epidemic and pandemic potential by the Global Influenza Surveillance and Response System. Available at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/379678
- WHO fact sheet for Influenza (Seasonal): https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal)
- WHO Routine influenza weekly updates. Available at:https://www.who.int/teams/global-influenza-programme/surveillance-and-monitoring/influenza-updates
- WHO Influenza surveillance outputs. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/global-influenza-programme/surveillance-and-monitoring/influenza-surveillance-outputs
- WHO Global COVID-19 Dashboard. Available at :https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases
- WHO Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) Epidemiological Updates. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports
- WHO Clinical practice guidelines for influenza. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240097759
- WHO Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) disease. Available at: https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-and-specifications/norms-and-standards/vaccine-standardization/respiratory-syncytial-virus-disease
- https://www.chinacdc.cn/jksj/jksj04_14249/
- US CDC Human Metapneumovirus. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/human-metapneumovirus/about/index.html
- American Lung Association. Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV) Symptoms and Diagnosis. Available at: https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/human-metapneumovirus-hmpv/symptoms-diagnosis
[1] China CDC Weekly Influenza Surveillance Report. Available at: https://www.chinacdc.cn/jksj/jksj04_14249/
[2] WHO Clinical practice guidelines for influenza. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240097759
Citable reference: World Health Organization (7 January 2025). Disease Outbreak News; Trends of acute respiratory infection, including human metapneumovirus, in the Northern Hemisphere. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2024-DON550