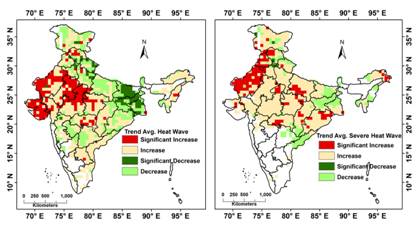
North-Western, Central, and further to south-central region of India are the new hotspot of intense heatwave events over the past half-century, said a study which found an increase in deadly Indian heat waves in recent years. The study also highlights the need for developing effective heat action plans in the three heatwave hotspot regions with a focus on different vulnerabilities among the inhabitants.
Heatwaves emerged as a deadly health hazard, claiming thousands of lives across the globe in recent decades, with episodes strengthening in frequency, intensity, and duration in the past half-century in India as well. This has caused severe impacts on health, agriculture, economy, and infrastructure. In such a scenario, it is extremely important to identify the most heatwave vulnerable regions of the country to prioritize immediate policy intervention and stringent mitigation and adaptation strategies.
A team of researchers led by Prof. R.K. Mall and including Saumya Singh and Nidhi Singh from the Department of Science & Technology, Govt. of India-Mahamana Centre of Excellence in Climate Change Research (MCECCR) at Banaras Hindu University studied the change in spatial and temporal trends in Heatwaves (HW) and Severe heatwaves (SHW) over the past seven decades in different meteorological subdivisions of India. This work has been supported under the Climate Change Program of the Department of Science & Technology. The study published in the journal “International Journal of Climatology” links the association of HW and SHW with mortality over India.
The study showed a shift in the Spatio-temporal trend of HW events from the eastern region of Gangetic West Bengal and Bihar to North-Western, Central and further to the south-central region of India. The research also observed an alarming southward expansion and a spatial surge in SHW events in the last few decades that may put a greater population at additional risk of heat stress in a region already characterized by low Diurnal temperature range (DTR), or the difference between the maximum and minimum temperatures within one day and high humidity. Importantly, the HW/SHW events were found to be positively correlated with mortality in Odisha and Andhra Pradesh, highlighting that human health is highly susceptible to severe heatwave disasters.
With an ever-increasing extreme-temperature threshold, a heat resilient future is the need of the hour. A dense population with an intensive outdoor work culture calls for equitable heat resilient mitigation and adaptation strategies covering each section of the society depending on their vulnerability. The study highlights the need for developing effective heat action plans in the three heatwave hotspot regions.
To mitigate future disastrous implications of exacerbated heat extremes and frame adequate adaptation measures in the wake of possible emergence of new hotspots, reliable future projections are needed. This motivated the research team consisting of Saumya Singh, Jiteshwar Dadich, Sunita Verma, J.V. Singh, and Akhilesh Gupta, and R. K. Mall to evaluate the regional climate models (RCM) over the Indian subcontinent to find the best performing RCM. These will help study the frequency, intensity, and spatial surge of heatwaves in the future. The study found models LMDZ4 and GFDL-ESM2M to be the best-performing ones in simulating heat waves over India in the present scenario, which can be reliably used for future projections as well. Thing study was recently published in an international journal, “Atmospheric Research”. The two models have laid the grounds for preparation for a heatwave resilient future.
Publication Link:
https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.6814 (International Journal of Climatology).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2020.105228 (Atmospheric Research)
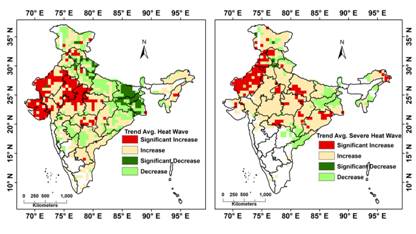
Fig. Long term trend in the seasonal heatwave and severe heatwave events
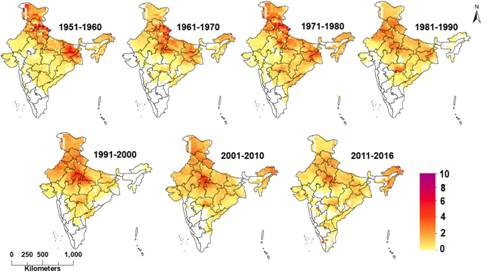
Fig. Spatio-temporal shift in the occurrence of Heat Wave Events over India