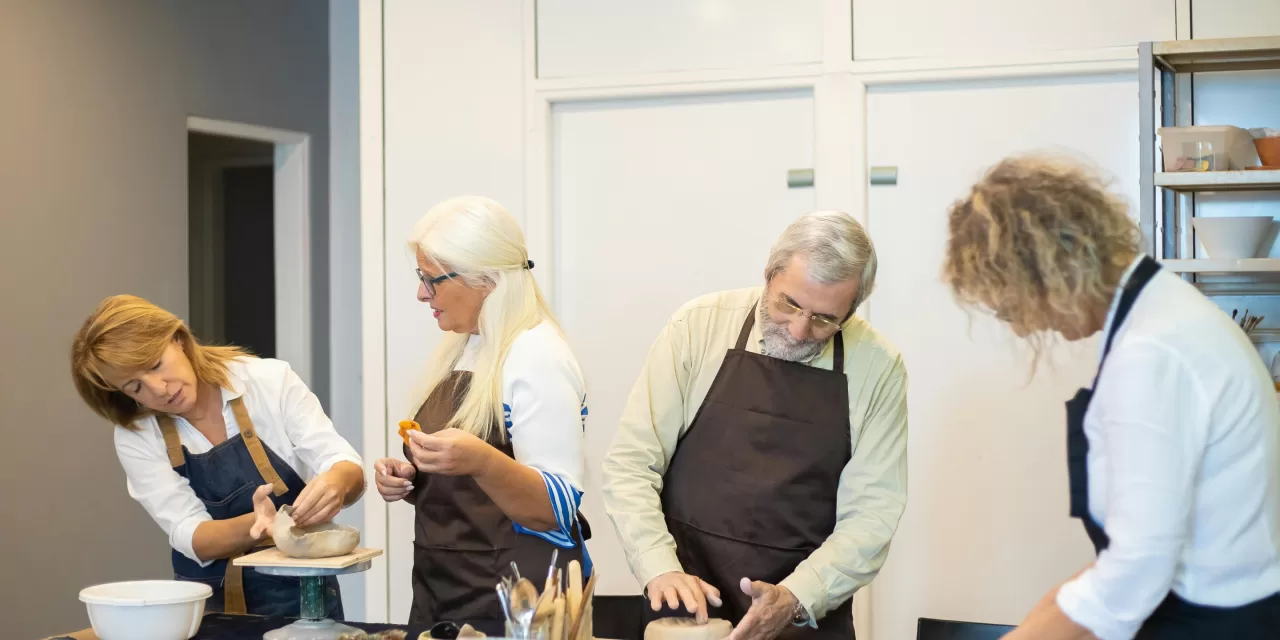
A groundbreaking study led by researchers at Queen Mary University of London has revealed that group arts interventions—such as painting, music, or dance—can significantly reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety among older adults. Published in Nature Mental Health, the findings provide compelling evidence for the mental health benefits of shared creative activities.
Depression and anxiety affect millions of older adults worldwide, with 7% of those aged 60 and over experiencing depression and 3.8% suffering from anxiety. Traditional treatments, such as medication and talking therapies, can be effective but are not always accessible or suitable for everyone due to potential side effects, costs, or reluctance to seek mental health support. This new research highlights the power of creative engagement in a social setting as an alternative approach.
A Comprehensive Analysis
The study, led by Ph.D. candidate Elizabeth Quinn, involved a meta-analysis of 39 studies across 21 countries, encompassing data from over 3,360 participants for depression and 949 participants for anxiety. The results were striking:
- Group arts interventions effectively reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety, even after adjusting for potential biases in publication.
- The effect sizes observed were comparable to those of traditional treatments such as antidepressants, therapy, and physical activity.
- Older adults in care homes showed even greater reductions in depression symptoms than those living in the community, emphasizing the role of these interventions in supporting vulnerable populations.
The Power of Creative Connection
One of the most notable aspects of the study was the consistency of benefits across different types of art, including painting, dancing, and making music. This suggests that the key factor in these interventions is the shared experience of creative expression rather than any specific artistic activity.
Dr. Janelle Jones, the study’s senior author, emphasized the significance of the findings: “Our research demonstrates that group arts interventions are an effective way to alleviate depression and anxiety among older adults. The combination of social interaction and creative engagement creates a unique synergy that benefits mental health.”
Implications for Mental Health Care
The study underscores the importance of integrating group arts interventions into mental health care strategies for older adults. The UK’s social prescribing initiative, which links patients to community-based activities for well-being, already incorporates arts interventions, but this study provides the robust evidence needed to solidify their role in health care policies.
“Arts interventions are not only accessible and cost-effective but also enjoyable,” Dr. Jones noted. “For older adults who may face barriers to traditional treatments, these activities provide a meaningful and engaging way to improve mental well-being.”
Addressing Social Isolation
The findings also highlight the significance of social interaction in mental health care. Older adults in care homes, who often experience higher levels of isolation, showed the most significant improvements, reinforcing the importance of community engagement in addressing mental health concerns.
Looking Ahead
The research team calls for further studies to explore the long-term benefits of group arts interventions and their potential applications for different age groups and settings. They hope that health care providers and policymakers will recognize the value of creative activities in mental health treatment plans.
For more details: Elizabeth A. Quinn et al, Group arts interventions for depression and anxiety among older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nature Mental Health (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s44220-024-00368-1
Disclaimer: This article summarizes recent research findings and is for informational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Individuals experiencing mental health concerns should consult a qualified health care provider for personalized support.