New Research Reveals the Potential of Circadian Nutrition to Alleviate Fatigue
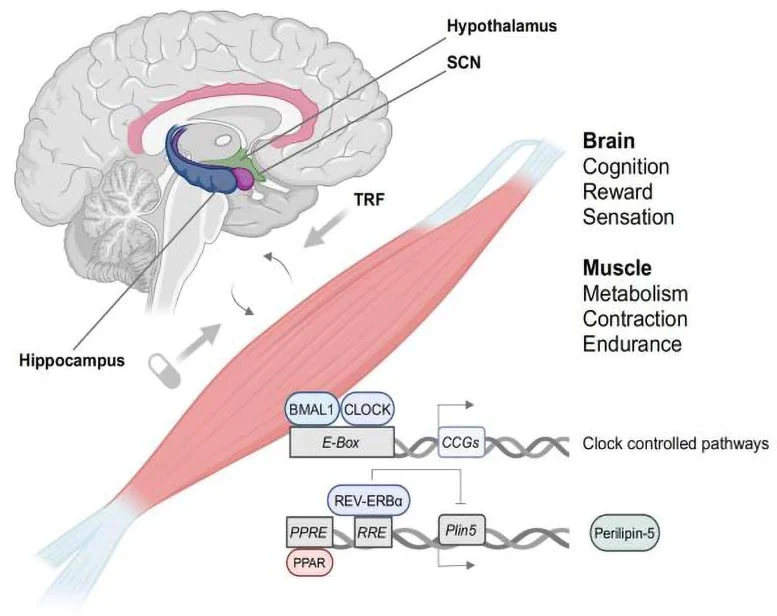
Fatigue, a pervasive issue affecting millions in industrialized societies, could soon be mitigated by an innovative approach: aligning our eating habits with our body’s natural circadian rhythms. New research led by Dr. Min-Dian Li from the Department of Cardiovascular Medicine at Southwest Hospital, China, highlights the powerful potential of time-restricted feeding (TRF) to reduce fatigue and improve both cognitive function and muscle endurance.
Circadian Rhythm and Fatigue
In today’s fast-paced world, fatigue is a major concern. It’s characterized by reduced muscle strength, persistent exhaustion, and diminished cognitive function. Although the root causes of fatigue have been elusive, new studies suggest a link between circadian rhythm disruptions and fatigue. The circadian rhythm governs many physiological processes, including sleep-wake cycles, metabolism, and muscle function. Disruptions to this rhythm, often caused by irregular sleeping and eating patterns, have been linked to a range of health issues, including fatigue.
A recent study sheds light on how circadian rhythms influence muscle endurance and cognitive function. The research suggests that adjusting eating patterns to align with the body’s internal clock could be a key strategy in managing fatigue. The study underscores the promise of circadian nutrition as a feasible lifestyle intervention that can restore energy levels and enhance overall well-being.
Time-Restricted Feeding: A Promising Solution
One particularly exciting finding from this research is the effectiveness of time-restricted feeding (TRF) in combating fatigue. TRF is an eating pattern that limits food intake to a specific time window each day, creating an intermittent feeding and fasting cycle. This approach is believed to optimize the body’s natural metabolic processes and promote better energy regulation. One of the most studied forms of TRF is the 16:8 method, where eating is restricted to an 8-hour window, followed by 16 hours of fasting.
Emerging evidence suggests that synchronizing meal times with the circadian rhythm, such as in night/active-phase restricted feeding (NRF), improves metabolic health, supports muscle endurance, and alleviates cognitive dysfunction. In animal studies, NRF has been shown to increase muscle endurance and improve the metabolic flexibility of mice, even in those on a high-fat diet. The 16:8 intermittent fasting method is particularly beneficial, boosting fat oxidation during the fasting phase and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
Scientific Insights on Muscle Endurance and Cognitive Function
The potential of circadian nutrition to combat fatigue extends beyond muscle endurance. The study reveals that TRF has also demonstrated a positive effect on cognitive function, supporting mental clarity and focus. This form of meal timing could help individuals battling fatigue both mentally and physically, providing a holistic approach to wellness.
Notably, in studies on aging mice, TRF was found to restore muscle strength by optimizing the coordination between the brain and muscle clocks. This offers hope for older individuals who experience a decline in physical function due to aging or chronic conditions.
Circadian Nutrition: A Sustainable and Accessible Solution
One of the most promising aspects of this research is its practicality. Time-restricted feeding is a simple, easily adoptable lifestyle change that doesn’t require drastic alterations to daily life. Unlike many pharmaceutical or medical interventions, circadian nutrition offers a non-invasive and sustainable way to manage fatigue. The evidence suggests that by respecting the body’s natural circadian rhythms, individuals can reduce the risk of fatigue-related health issues, such as metabolic diseases, and improve overall quality of life.
As the research progresses, the scientific community is optimistic that circadian nutrition could provide a low-cost, accessible solution for the growing global challenge of fatigue. The hope is that these findings could eventually lead to widespread changes in dietary recommendations, helping individuals feel more energized and better equipped to manage the demands of modern life.
Conclusion
Circadian nutrition, particularly time-restricted feeding, is emerging as a promising intervention in the fight against fatigue. By aligning food intake with the body’s natural rhythms, individuals could experience improved muscle endurance, better cognitive function, and enhanced overall well-being. As more clinical trials and studies continue to explore the potential of this approach, it offers a hopeful glimpse into a future where fatigue can be managed with a simple but powerful lifestyle change.
For further reading, the full study, Circadian Nutrition: Is Meal Timing an Elixir for Fatigue? by Zhihui Zhang, Lu Yan, Jonas T. Treebak, and Min-Dian Li, can be found in Science Bulletin. DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.11.043.
Source:
Science Bulletin, November 28, 2024
Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Center for Circadian Metabolism and Cardiovascular Disease, Southwest Hospital, China