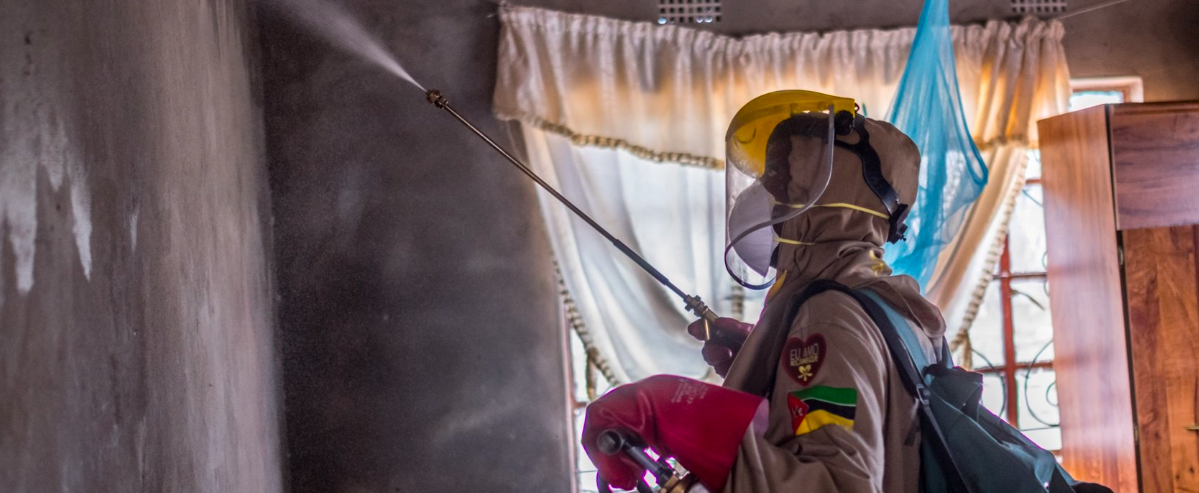
Equitable access to life-saving malaria tools is key to reversing trends
“No one should die of malaria; yet the disease continues to disproportionately harm people living in the African region, especially young children and pregnant women,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General. “An expanded package of lifesaving tools now offers better protection against the disease, but stepped-up investments and action in high-burden African countries are needed to curb the threat.”
Clear progress in many countries
As of November 2024, 44 countries and 1 territory had been certified malaria-free by WHO, and many more are steadily progressing towards the goal. Of the 83 malaria-endemic countries, 25 countries now report fewer than 10 cases of malaria a year, an increase from 4 countries in 2000.
Since 2015, the WHO African Region has also achieved a 16% reduction in its malaria mortality rate. However, the estimated 2023 mortality rate of 52.4 deaths per 100 000 population at risk is still more than double the target level of 23 deaths per 100 000 population set by the Global technical strategy for malaria 2016-2030, and progress must be accelerated.
Earlier this year, Ministers of Health from 11 African countries that account for two-thirds of the global malaria burden (Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, United Republic of Tanzania and Uganda) signed a declaration pledging to sustainably and equitably lower the disease burden and address the root causes by strengthening national health systems, enhancing coordination and ensuring the strategic use of information, among other actions.
Broader use of effective tools offers renewed hope
Alongside stepped-up political commitment, the wider deployment of WHO-recommended tools is poised to drive further gains in malaria-endemic countries. As of December 2024, 17 countries had introduced malaria vaccines through routine childhood immunization. The continued scale-up of the vaccines in Africa is expected to save tens of thousands of young lives every year.
New-generation nets, which provide better protection against malaria than pyrethroid-only nets, are becoming more widely available, supporting efforts to combat mosquito resistance to pyrethroids. In 2023, these new types of nets accounted for 78% of the 195 million nets delivered to sub-Saharan Africa, an increase from 59% in 2022.
Funding remains a major barrier to future progress
Funding for malaria control globally remains inadequate to reverse current trends, especially in high-burden African countries. In 2023, total funding reached an estimated US$ 4 billion, falling far short of the year’s funding target of US$ 8.3 billion set by the Global technical strategy. Insufficient funding has led to major gaps in coverage of insecticide-treated nets, medicines, and other life-saving tools, particularly for those most vulnerable to the disease.
Beyond funding, malaria-endemic countries continue to grapple with fragile health systems, weak surveillance, and rising biological threats, such as drug and insecticide resistance. In many areas, conflict, violence, natural disasters, climate change and population displacement are exacerbating already pervasive health inequities faced by people at higher risk of malaria, including pregnant women and girls, children aged under 5 years, Indigenous Peoples, migrants, persons with disabilities, and people in remote areas with limited healthcare access.
Bridging gaps in malaria care through equity-focused action
This year’s World malaria report highlights the need for a more inclusive and effective response to reach those most vulnerable to the disease. WHO urges countries to prioritize primary health care as the foundation of equitable and efficient health systems. Countries are encouraged to adopt strategies that address the root causes of malaria by addressing gender inequities and other determinants of health.
WHO is also calling for investments in robust data systems that are capable of monitoring health inequalities, including through the collection and analysis of data disaggregated by sex, age and other social stratifiers. Equity, gender equality and human rights should be the cornerstones of antimalarial innovation, with people most impacted by the disease engaged in the design and evaluation of new tools and approaches.