Phosphine gas, a chemical widely used in industrial fumigation, poses a serious threat to human health when improperly handled. This toxic gas has been linked to multiple fatalities in both industrial and residential settings. Notably, in 1980, two children and 29 crew members aboard a grain freighter were poisoned after prolonged exposure to phosphine, leading to one child’s death. A more recent tragedy occurred in 2024, when a family in the Dominican Republic succumbed to phosphine poisoning after fumigation of their apartment to eliminate a woodworm infestation.
The dangers of phosphine, also known as PH₃, have long been recognized, yet its use continues in various industries, from semiconductor production to pest control. Most notably, phosphine is used as an insecticide, rodenticide, and fumigant in the agricultural and forestry sectors to prevent infestations of grains and wood. However, its toxic effects on the human body have raised concerns about safety and the need for better preventative measures.
Phosphine is colorless and odorless in its pure form, though it can emit a garlic or rotten fish smell in its commercial grade. Even in small concentrations—such as the 0.3 parts per million regulated by U.S. safety standards—exposure to phosphine can have severe health consequences. Symptoms of poisoning include nausea, chest tightness, difficulty breathing, abdominal pain, and in extreme cases, damage to the heart, liver, and kidneys, which can lead to death.
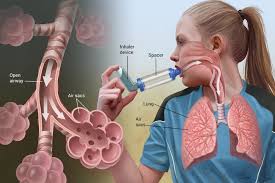
The toxicity of phosphine has prompted researchers, including pharmaceutical scientists, to investigate potential treatments and preventative strategies. Dr. Akshay Minhas, a pharmaceutical scientist studying the effects of chemicals on the human body, is currently developing inhalable therapies aimed at mitigating the lung damage caused by phosphine exposure. These therapies could help reduce inflammation and improve lung function for those affected by this hazardous gas.
Despite the advances in medical research, there is currently no antidote for phosphine poisoning, and treatment mainly focuses on managing symptoms. Workers exposed to phosphine are advised to wear protective respiratory equipment and follow safety guidelines to reduce the risk of exposure. However, the increasing number of deaths associated with phosphine poisoning highlights the need for greater awareness and more effective regulations surrounding its use.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only. Always consult professionals and follow safety guidelines when handling chemicals like phosphine.