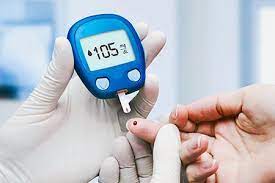
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), traditionally pivotal tools in diabetes management, are now finding a new frontier in combating obesity-related health risks. Recent reports indicate a surge in off-label use of CGMs to aid individuals on the cusp of developing diabetes, while also shedding light on undiagnosed cases of the condition.
At the forefront of this trend is Lori Wenz, a nurse practitioner at Western Colorado Weight Care, who presented on the topic at the Obesity Medicine (OMA) 2024 conference in Grand Junction, Colorado. According to Wenz, CGMs offer a unique avenue for individuals struggling with obesity to monitor their glucose levels, potentially reversing the path towards diabetes through lifestyle interventions.
Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention underscores the urgency of this approach, revealing that a significant portion of adults in the United States are unaware of their prediabetes or diabetes status. Wenz highlights that a staggering 90% of individuals with diabetes are either overweight or obese, emphasizing the critical need for proactive measures.
The adoption of CGMs in obesity management has surged in recent years, driven by advancements in technology and increased affordability. Wenz notes that while these devices are officially sanctioned for diabetes management, their off-label use in obesity care is gaining traction among both clinicians and patients.
Dr. Shagun Bindlish of One Medical echoes this sentiment, emphasizing the importance of early intervention in obesity-related glucose abnormalities. She emphasizes that CGMs provide individuals with real-time insights into their metabolic health, empowering them to make informed decisions about their lifestyle choices.
The recent FDA approval of the Dexcom Stelo Glucose Biosensor System marks a significant milestone in CGM accessibility. Unlike previous models requiring a prescription, this over-the-counter device targets a broader demographic, including individuals without diabetes seeking to monitor their blood sugar levels. Jeff Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health, hails this development as a step towards promoting health equity.
However, experts caution that CGM usage in obesity management is not without its challenges. Wenz highlights concerns regarding the interpretation of glucose readings in individuals without diabetes, as well as the potential for excessive glucose control leading to unhealthy behaviors. Nevertheless, she remains optimistic about the transformative potential of over-the-counter CGMs in empowering individuals to take control of their health destiny.
Dr. Alaina Vidmar, an expert in pediatric obesity management, underscores the broader implications of CGM integration in preventive healthcare. Drawing from her research on youth with obesity, Vidmar emphasizes the educational and motivational benefits of real-time glucose monitoring. She stresses the importance of holistic approaches to obesity management, encompassing innovative technologies alongside behavioral interventions.
As over-the-counter CGMs enter the market, the hope is to democratize access to this transformative technology across age groups and weight categories. While challenges remain, the growing acceptance of CGMs in obesity management signals a paradigm shift towards proactive healthcare interventions aimed at curbing the rising tide of metabolic disorders.
In an era defined by data-driven healthcare, over-the-counter CGMs represent a promising tool in the fight against obesity-related health risks, offering individuals the opportunity to rewrite their health narrative one glucose reading at a time.