March 7, 2025 – A new oral vaccine for norovirus has demonstrated strong safety and immune response in a Phase 1 clinical trial, according to research published by scientists at Vaxart, a biotechnology company specializing in oral vaccines. The findings mark a promising step toward preventing norovirus infections, which are a leading cause of acute gastroenteritis worldwide.
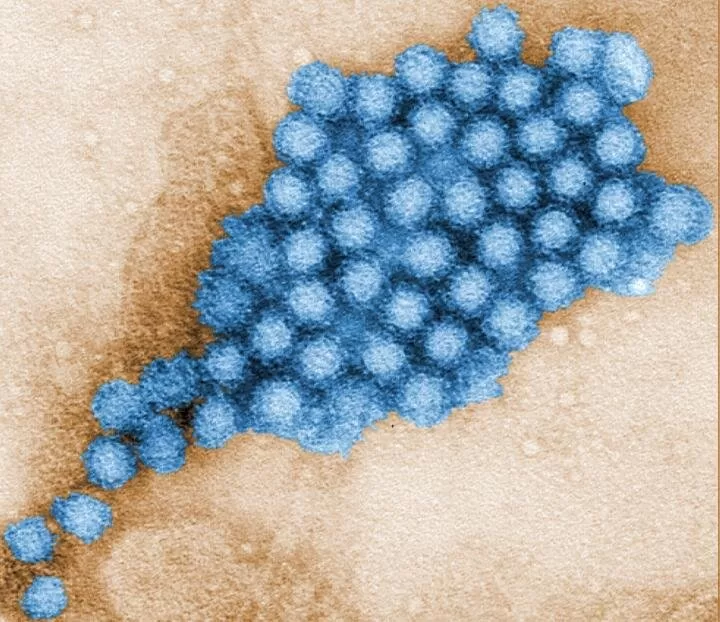
Norovirus, often referred to as the “stomach flu,” is highly contagious and can spread through contaminated food, water, and surfaces. The virus causes symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain, leading to significant public health burdens, particularly in healthcare settings and among young children and the elderly.
The trial involved 58 healthy adult participants who received the oral norovirus vaccine. The results showed that the vaccine was well tolerated, with only mild side effects reported, such as headache and fatigue. Furthermore, participants exhibited a robust immune response, with significant increases in both antibody and T-cell activity against norovirus.
Dr. Sean Tucker, Chief Scientific Officer at Vaxart, emphasized the advantages of an oral vaccine, stating that it could simplify distribution and increase accessibility compared to traditional injectable vaccines. “An oral norovirus vaccine has the potential to improve global vaccination efforts by eliminating the need for needles and offering greater convenience for mass immunization campaigns,” Dr. Tucker said.
Norovirus infections lead to approximately 685 million cases globally each year, with severe cases requiring hospitalization. Currently, there is no approved vaccine for norovirus, making this breakthrough a crucial development in infectious disease prevention.
While the early results are promising, further trials will be needed to confirm the vaccine’s efficacy in larger populations and high-risk groups. Vaxart plans to advance the vaccine into Phase 2 trials in the coming months.
Disclaimer: This article is based on preliminary findings from a Phase 1 clinical trial. Further studies are required to determine the long-term efficacy and safety of the oral norovirus vaccine. Readers are advised to consult healthcare professionals for medical advice related to norovirus and vaccination options.