Rourkela, Mar 28—A groundbreaking advancement in biomedical engineering has emerged from the National Institute of Technology (NIT) Rourkela, where researchers have successfully developed a novel natural bioink designed to revolutionize the 3D bioprinting of bone tissue. This innovation promises to significantly enhance tissue engineering and regenerative medicine practices.
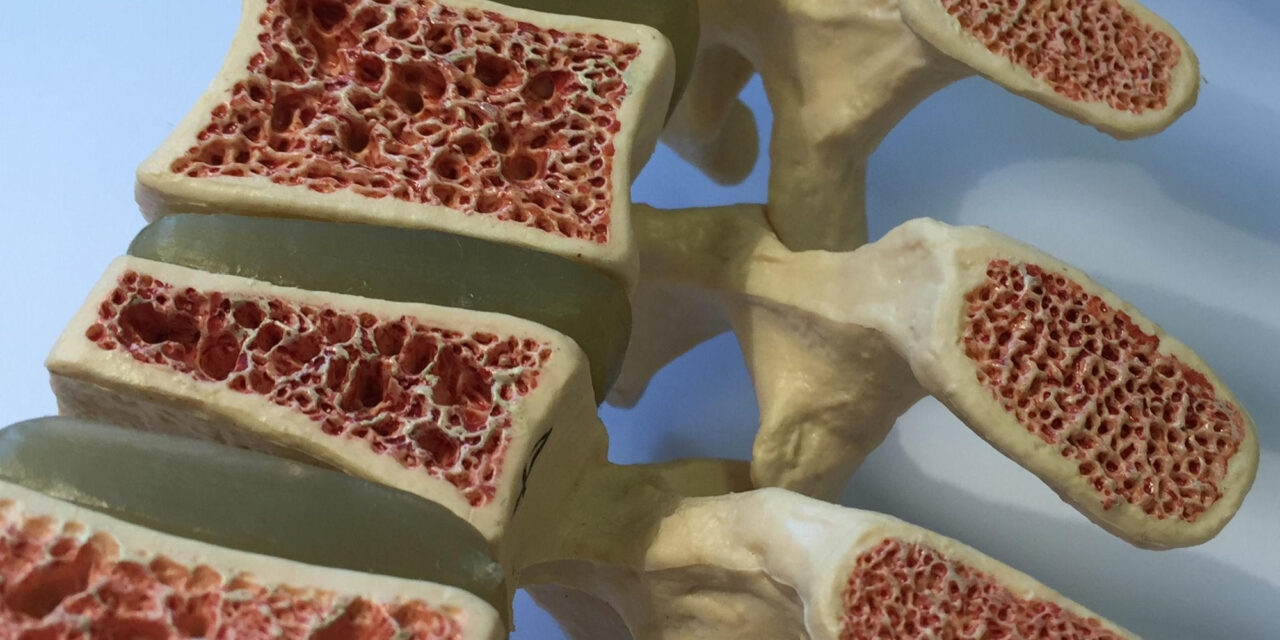
The newly developed bioink, formulated using natural polymers and bioactive components, is engineered to enable precise 3D bioprinting of bone tissue, facilitating the regeneration of damaged or lost bone structures. Researchers assert that this bioink exhibits superior biocompatibility, mechanical strength, and osteoinductivity compared to traditional bioinks.
Dr. Anil Kumar, the Lead Researcher and Professor of Biomedical Engineering at NIT Rourkela, explained that the bioink’s composition is inspired by the natural structure of bone tissue, which comprises collagen, hydroxyapatite, and various organic materials. “Our bioink effectively replicates the natural bone matrix, creating an ideal environment for bone cell growth and proliferation,” he stated.
This innovative bioink is poised to transform bone tissue engineering by offering a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to current methods. It is particularly advantageous for patients needing bone grafts or implants due to injuries, congenital defects, or degenerative diseases.
The research team is currently conducting tests to assess the bioink’s suitability for large-scale applications and intends to collaborate with medical institutions to initiate clinical trials. If these trials prove successful, this breakthrough could pave the way for the development of advanced prosthetics, implants, and tissue repair solutions.
The researchers are optimistic that their innovation will significantly contribute to regenerative medicine, offering renewed hope for patients suffering from bone-related ailments.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is based on the details provided and is for informational purposes only. The research is still in development, and the claims made are subject to further testing and validation. The success of clinical trials and the eventual availability of this bioink for widespread medical use cannot be guaranteed at this time. Readers should consult with healthcare professionals for medical advice and treatment options.