December 16, 2024
A groundbreaking compound, HPH-15, developed by scientists at Kumamoto University, is showing tremendous promise as a more effective treatment for diabetes, outperforming the current standard of care, metformin. In preclinical trials, HPH-15 demonstrated remarkable abilities to reduce both blood glucose levels and fat accumulation, offering a potential revolution in diabetes care.
A Dual-Action Treatment for Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes affects millions globally and often leads to severe complications such as fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, and obesity. Current treatment methods, including metformin, have limited success in addressing these issues simultaneously. However, the new compound, HPH-15, has proven to be far more effective in reducing blood glucose and fat while also providing additional therapeutic benefits.
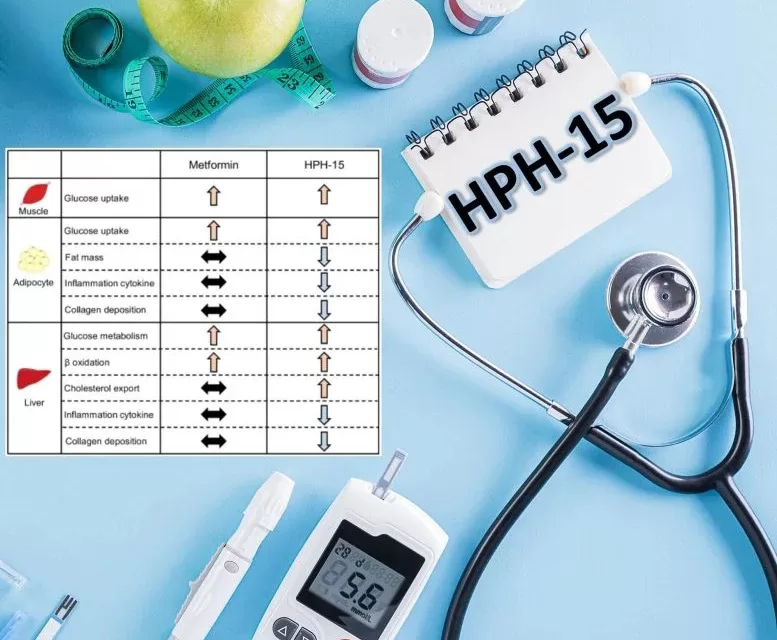
Developed by a team led by Visiting Associate Professor Hiroshi Tateishi and Professor Eiichi Araki, HPH-15 targets AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a crucial protein in regulating energy balance. The compound activates AMPK at far lower doses than metformin, enabling better glucose uptake in liver, muscle, and fat cells. In addition to improving glucose control, HPH-15 dramatically reduced fat accumulation in obese mice fed a high-fat diet, proving its potential to combat both diabetes and obesity simultaneously.
Key Research Findings
The study, published in the prestigious journal Diabetologia, highlights several key findings from the research:
- Enhanced Efficacy: HPH-15 activated AMPK and promoted glucose uptake at concentrations 200 times lower than those required for metformin to be effective.
- Fat Reduction: HPH-15 significantly reduced subcutaneous fat by 44% and showed superior effectiveness in combating fatty liver compared to metformin in preclinical trials.
- Safer Profile: The compound showed lower levels of lactic acid production—a potential risk associated with metformin—suggesting a reduced risk of lactic acidosis, a serious side effect that limits the use of metformin in some patients.
A Promising Future for Diabetes Treatment
The innovative properties of HPH-15 could redefine the landscape of diabetes management. By combining blood sugar control with the prevention of obesity-related complications, this compound promises to not only manage diabetes but also address some of its most debilitating side effects, such as fatty liver and insulin resistance.
“This compound holds transformative potential for diabetes treatment, offering benefits beyond just blood sugar regulation,” said Professor Mikako Fujita from the Faculty of Life Sciences at Kumamoto University.
Given the significant benefits of HPH-15 in early trials, there is great optimism that this compound could soon become a cornerstone of diabetes treatment. The research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, and other prestigious organizations.
As the compound moves forward into further clinical testing, it could become a safer, more effective alternative to existing treatments, potentially changing the lives of millions affected by diabetes worldwide.
Reference:
“An antifibrotic compound that ameliorates hyperglycaemia and fat accumulation in cell and HFD mouse models” by Tsugumasa Toma, Nobukazu Miyakawa, Yuiichi Arakaki, Takuro Watanabe, Ryosei Nakahara, Taha F. S. Ali, Tanima Biswas, Mikio Todaka, Tatsuya Kondo, Mikako Fujita, Masami Otsuka, Eiichi Araki, and Hiroshi Tateishi, Diabetologia, September 9, 2024. DOI: 10.1007/s00125-024-06260-y.