In a groundbreaking initiative, researchers have demonstrated the potential of AI-generated social media influencers to spread cancer prevention messages effectively and at a low cost. The study, published in the European Journal of Cancer, introduces “Wanda,” a virtual influencer designed using generative AI to target specific demographics and promote awareness about cancer risk factors.
The Rising Need for Cancer Prevention
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide, with many cases linked to modifiable risk factors like smoking, poor diet, and alcohol consumption. While advances in therapy have improved survival rates, prevention is crucial to reducing the overall cancer burden. Studies show that a significant proportion of cancer deaths—37% in females and 50% in males—could be attributed to preventable causes.
Traditional prevention campaigns, however, often fail to engage younger audiences who favor digital-first communication methods. Research institutes face challenges competing with the massive marketing power of industries such as tobacco and alcohol. The study explores an innovative, cost-effective solution to this problem: AI-generated influencers.
Wanda’s Campaign: Reaching Audiences Through Instagram
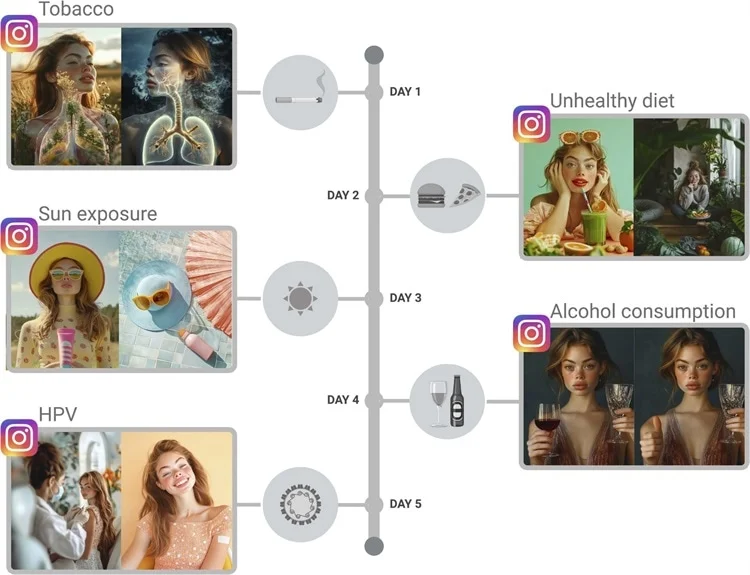
Using Midjourney, a generative AI tool, the researchers created Wanda, a young female character with a consistent appearance and relatable persona. Over five days, Wanda’s Instagram account featured posts addressing key cancer risk factors: alcohol, human papillomavirus (HPV), unhealthy diets, tobacco use, and sun exposure. Each post included AI-generated images and concise captions with preventive messages.
To amplify Wanda’s reach, the team allocated €100 to advertising, using both automated and targeted approaches on Instagram. While the automated approach relied on Instagram’s algorithm to find an audience, the targeted strategy focused on specific age groups and interests.
Key Findings
The campaign achieved 9,902 recognitions in 10 days, with nearly equal reach from both advertising approaches. Notable results included:
- Audience Engagement: Posts on HPV garnered the highest engagement, while content about sun exposure saw the least interaction.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Targeting younger audiences was more economical, especially for messages about tobacco prevention (€0.006 per user).
- Demographic Insights: Targeted ads effectively reached individuals aged 34 and below, while automated ads had a broader reach among those over 35. Female users were more likely to engage with prevention messages.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its success, the study highlighted hurdles such as building trust and perceived authenticity with AI influencers. The lack of engagement on sun-related cancer risks also suggested the need for more innovative messaging strategies.
The researchers emphasize the scalability of AI influencers like Wanda for health communication. However, they call for further studies to explore interactive features and personalized content to strengthen user connections and long-term impact.
A Step Toward the Future of Health Promotion
With minimal investment, Wanda’s campaign demonstrated the immense potential of AI-driven health influencers to reach and educate diverse audiences. As digital platforms continue to dominate communication, virtual influencers may become invaluable tools in the fight against cancer and other preventable diseases.
For more information, read the full study in the European Journal of Cancer: DOI: 10.1016/j.ejca.2025.115251.