Nabilatuk and Amudat Districts Hit Hard by Measles Epidemic
Uganda’s Ministry of Health has confirmed the deaths of five children due to a measles outbreak in the semi-arid northeastern districts of Nabilatuk and Amudat. Four of the fatalities were recorded in Nabilatuk, while the remaining death occurred in Amudat. As of Wednesday, 11 measles cases were hospitalized, with an additional five cases treated at outpatient departments, according to the ministry’s situation update.
The outbreak was first confirmed in Amudat on January 6, with the ministry reporting 147 cumulative cases and a case fatality rate (CFR) of 2.7% in Nabilatuk, alongside 47 cumulative cases in Amudat. The Amudat District Task Force convened its initial meeting on January 15 to coordinate efforts for disease prevention and control.
The measles epidemic adds to Uganda’s broader public health challenges, as the Ministry of Health reported measles outbreaks in 56 districts across the country last year.
What You Need to Know About Measles
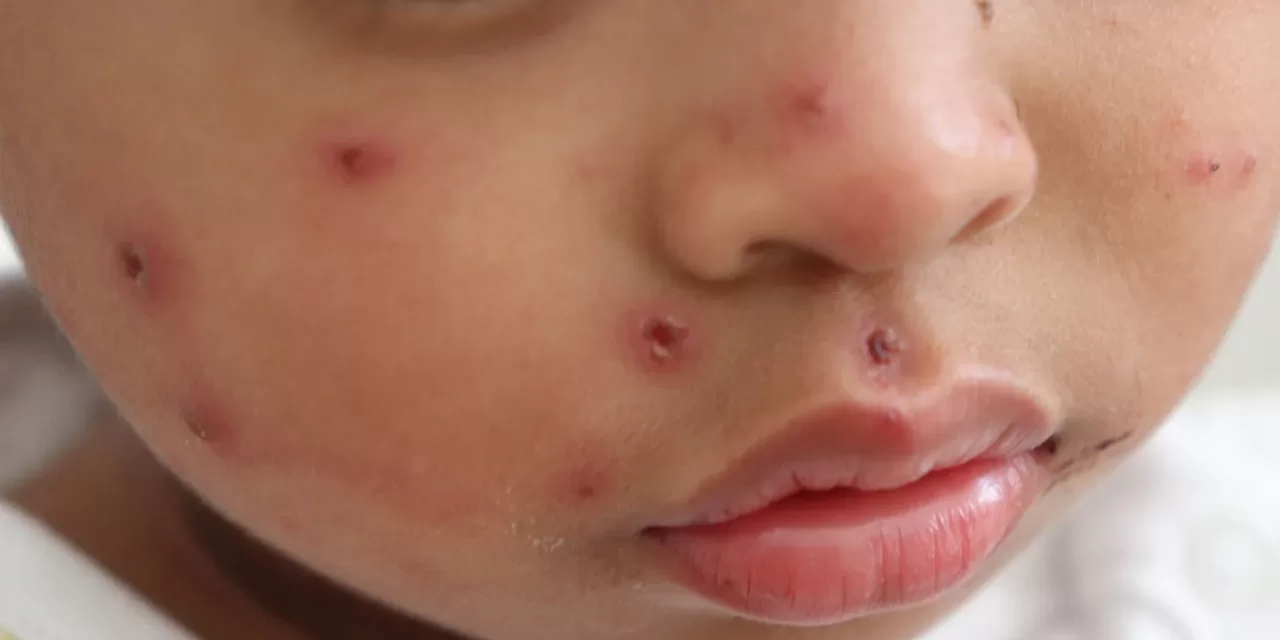
Measles is a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects children. The World Health Organization (WHO) describes measles as easily transmissible through respiratory droplets when an infected individual coughs, sneezes, or breathes. Symptoms include high fever, cough, runny nose, and a characteristic rash. Severe cases can lead to complications and even death.
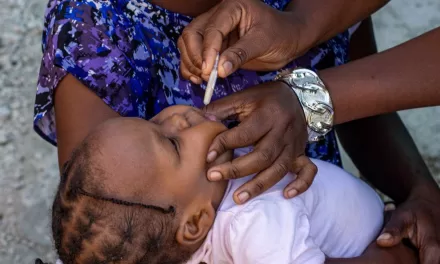
Vaccination remains the most effective defense against measles. The measles vaccine, introduced in 1963, has significantly reduced global cases and deaths. Prior to widespread immunization, measles caused major epidemics every two to three years, resulting in an estimated 2.6 million deaths annually. In 2023, the disease still claimed an estimated 107,500 lives worldwide, most of whom were children under five years of age.
Efforts to Combat the Outbreak
Health authorities in Amudat and Nabilatuk are mobilizing resources and implementing measures to curb the spread of the virus. However, challenges persist, including ensuring adequate vaccine coverage and timely access to healthcare services in remote areas.
As Uganda battles this outbreak, the importance of vaccination campaigns cannot be overstated. Health experts emphasize the need for global cooperation to ensure equitable access to vaccines, especially in regions prone to outbreaks.
Disclaimer: This article is based on information from Uganda’s Ministry of Health and the World Health Organization. The content is intended for informational purposes and should not substitute professional medical advice. For personal health concerns or vaccination inquiries, consult a healthcare provider. The statistics and data mentioned are accurate as of the time of reporting.