A groundbreaking study led by Prof. Li Hai and his team at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has unveiled an innovative framework aimed at revolutionizing the early detection and assessment of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The research, published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, introduces DEMENTIA, a hybrid multi-task learning framework that integrates speech, text, and expert knowledge for more accurate and interpretable AD detection.
As the global population ages, the prevalence of AD continues to rise, making early detection vital for improving patient outcomes. One of the earliest signs of cognitive decline is language deterioration. Although automated speech analysis offers a promising non-invasive method for detecting AD, existing approaches struggle with challenges such as complexity, poor interpretability, and limited data integration, which affect both accuracy and clinical applicability.
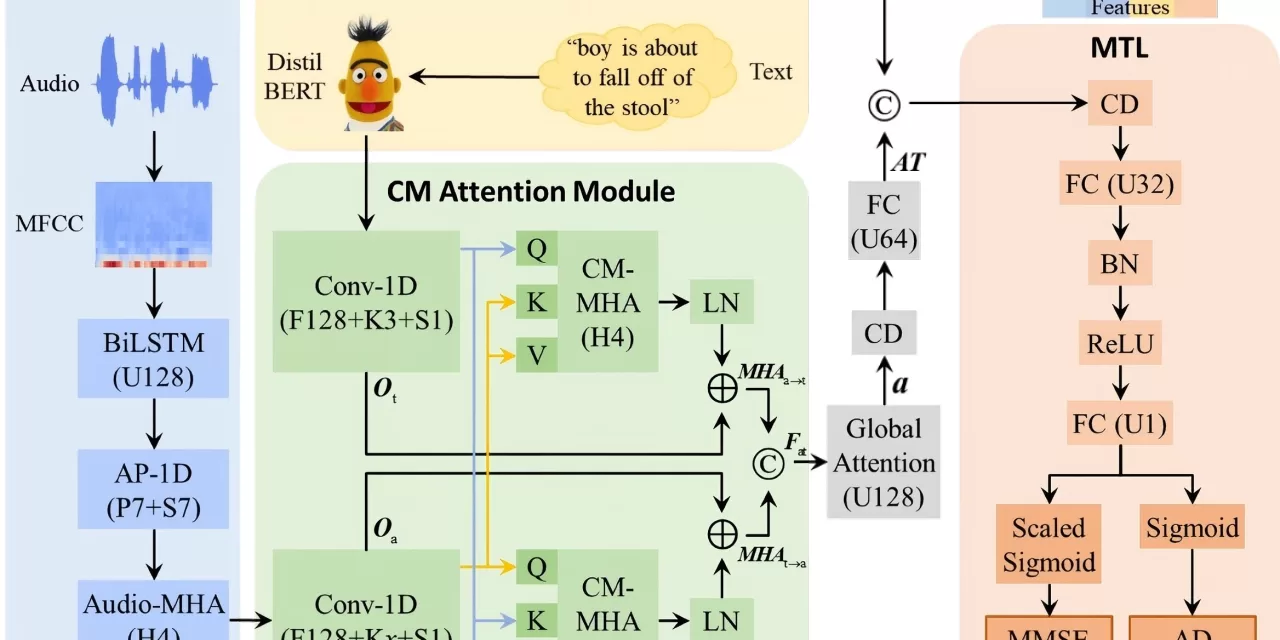
To address these issues, Prof. Li Hai’s team developed the DEMENTIA framework, which combines advanced large language model technologies with a hybrid attention mechanism. This novel method captures intricate intra- and inter-modal interactions, improving detection accuracy while enhancing the model’s clinical interpretability. The framework not only predicts cognitive function scores but also demonstrates robust decision-support capabilities, making it adaptable across diverse datasets.
The DEMENTIA approach paves the way for a more reliable, interpretable solution to AD detection, offering valuable insights into cognitive decline. This innovative framework highlights the potential of speech-based tools in improving early screening for AD, ultimately providing significant scientific and societal benefits as we face an aging population.
Disclaimer: This article summarizes the findings from the study DEMENTIA: A Hybrid Attention-Based Multimodal and Multi-Task Learning Framework With Expert Knowledge for Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment From Speech, by Zhenglin Zhang et al., published in the IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics (2024). The information provided is based on the research and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult healthcare professionals for medical concerns.