Introduction
Recent research presented at the ATS 2024 International Conference highlights a significant gap in the adoption of optimal asthma treatment regimens among older adults. Despite updated guidelines recommending the use of Single Maintenance And Relief Therapy (SMART) inhalers for managing moderate to severe asthma, healthcare providers appear hesitant to transition older patients to these new protocols.
The SMART Approach
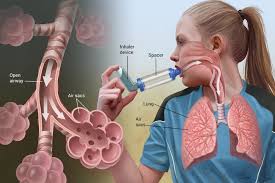
SMART inhalers combine a corticosteroid with a long-acting beta agonist (LABA) in a single device, such as Symbicort or Dulera. These inhalers serve both as maintenance treatments, taken twice daily, and as rescue inhalers during asthma attacks. The approach has demonstrated efficacy in reducing asthma exacerbations compared to traditional maintenance and rescue inhaler combinations.
Research Findings
A study led by Zoe Zimmerman, BS, and Dr. Sandra Zaeh from Yale University School of Medicine examined the implementation of SMART among patients visiting academic pulmonary and allergy clinics between 2021 and 2023. The findings reveal that only 14.5 percent of adult patients with moderate or severe asthma received SMART inhalers as recommended. Furthermore, over 40 percent of clinicians surveyed had not yet adopted SMART as the standard therapy.
Barriers to Adoption
According to the study, older patients and those insured by Medicare were significantly less likely to receive SMART prescriptions. Zimmerman suggests that providers may be reluctant to change treatment regimens for older individuals who have been accustomed to traditional inhaler therapies for years.
Dr. Zaeh emphasized the challenges in guideline adoption, noting that it often takes many years for new recommendations to be widely adopted by healthcare providers. Despite high awareness (93 percent) of SMART among surveyed clinicians, practical barriers such as insurance coverage and patient education hinder widespread implementation.
Implications for Asthma Management
The discordance between guideline recommendations and clinical practice underscores the need for targeted strategies to facilitate the adoption of SMART inhalers. Addressing barriers such as insurance formulary coverage, patient education on inhaler transitions, and clinician support through decision support tools could enhance the uptake of these beneficial therapies.
Conclusion
As asthma management evolves with updated guidelines advocating for SMART inhalers, bridging the gap between knowledge and practice is crucial. The research highlights not only the potential benefits of SMART in improving asthma outcomes but also the imperative to overcome implementation challenges for better patient care.
In summary, while advancements in asthma treatment offer promising outcomes, ensuring equitable access and adoption across all patient demographics remains a critical goal for healthcare providers and policymakers alike.