In a significant advancement for nutrition science, a recent review article published in Frontiers in Nutrition presents a comprehensive analysis of the health benefits and risks associated with fermented foods (FFs). This study, spearheaded by a large international research team, highlights the critical role of FFs not only in promoting human health but also in addressing broader societal issues such as planetary health and sustainable food systems.
The Role of Fermented Foods
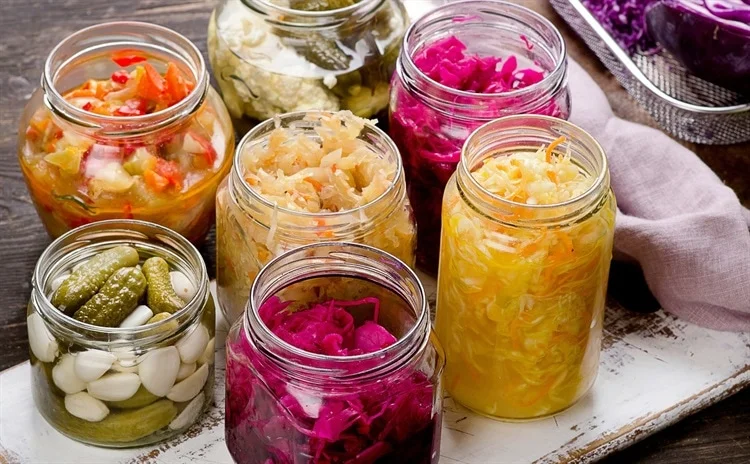
As modern diets increasingly shift towards processed foods, there is a growing need to sustain and enhance our food sources with diverse nutrients and beneficial microbes. Fermented foods, known for their extended shelf life and rich microbial content, are emerging as a key component in this dietary transition. They offer numerous benefits including the presence of live microbes, bioactive compounds, and essential vitamins.
PIMENTO Initiative: A European Endeavor
To systematically evaluate the health impacts of FFs, the PIMENTO (Promoting Innovation of Fermented Foods) initiative has been launched. This European project aims to consolidate emerging evidence from various fields, including foodomics, food ecosystems, nutrigenomics, and food microbiology, to provide a holistic understanding of FFs.
The initiative’s Working Group 3 (WG3) is tasked with assessing the health risks and benefits of FFs through 16 interconnected reviews. These reviews are guided by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) guidelines and cover a wide range of health-related topics.
Key Areas of Focus
- Gastrointestinal Health: A systematic review will explore whether FFs improve normal defecation and alleviate gastrointestinal discomfort in healthy adults.
- Food Allergies: The initiative will assess the impact of FFs on food allergy symptoms, particularly in populations at higher risk.
- Pathogenic Diseases: Research will focus on the potential of FFs to prevent conditions such as bacterial vaginosis and vulvovaginal candidiasis, which are prevalent among women and can lead to other health complications.
- Metabolic Health: The review will investigate whether FFs influence insulin sensitivity and blood glucose levels, addressing concerns related to type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Health: The effects of fermented dairy products on blood lipid levels will be evaluated, contributing to our understanding of their role in heart health.
- Bone Health: The initiative will examine how FFs affect calcium absorption and bone health, especially in populations at risk of osteoporosis.
- Cognitive Performance: The potential of FFs to benefit cognitive function, particularly in individuals with mild cognitive impairment, will be assessed.
- Bioactive Compounds: The review will address the relationship between fermentation-derived bioactive compounds and their health effects.
- Vitamin Fortification: Research will evaluate whether FFs can effectively address vitamin deficiencies.
- Iron Absorption: The impact of bread and sourdough fermentation on iron status and absorption will be explored.
- Ethnic Fermented Foods: The health benefits of traditional ethnic FFs like kimchi and koumiss will be examined, highlighting the importance of preserving these cultural foods.
- Mortality Risk: The study will investigate how FFs affect overall mortality risk.
- Personalized Nutrition: A review will consider how FFs can be tailored to individual health needs and characteristics.
- Food Safety: The safety of FFs will be scrutinized to ensure that new fermentation processes and products do not pose risks.
- Novel Fermented Foods: The effects of newly developed FFs will be assessed for their functional properties and health benefits.
- Fermented Whey: The health effects of fermented whey will be investigated as part of the review process.
Implications and Future Directions
The findings from this extensive review will be instrumental in shaping future research and public health policies. By providing a strategic roadmap for integrating FFs into public health frameworks, the PIMENTO initiative aims to align FF innovations with sustainable development goals.
The comprehensive and harmonized results from these reviews are expected to define new research directions and guide policy-making, ensuring that the health benefits of fermented foods are maximized while addressing potential risks.
For more detailed information, refer to the original article: Todorovic S, Akpinar A, Assunção R, et al. Health benefits and risks of fermented foods—the PIMENTO initiative. Frontiers in Nutrition, 2024. DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1458536.