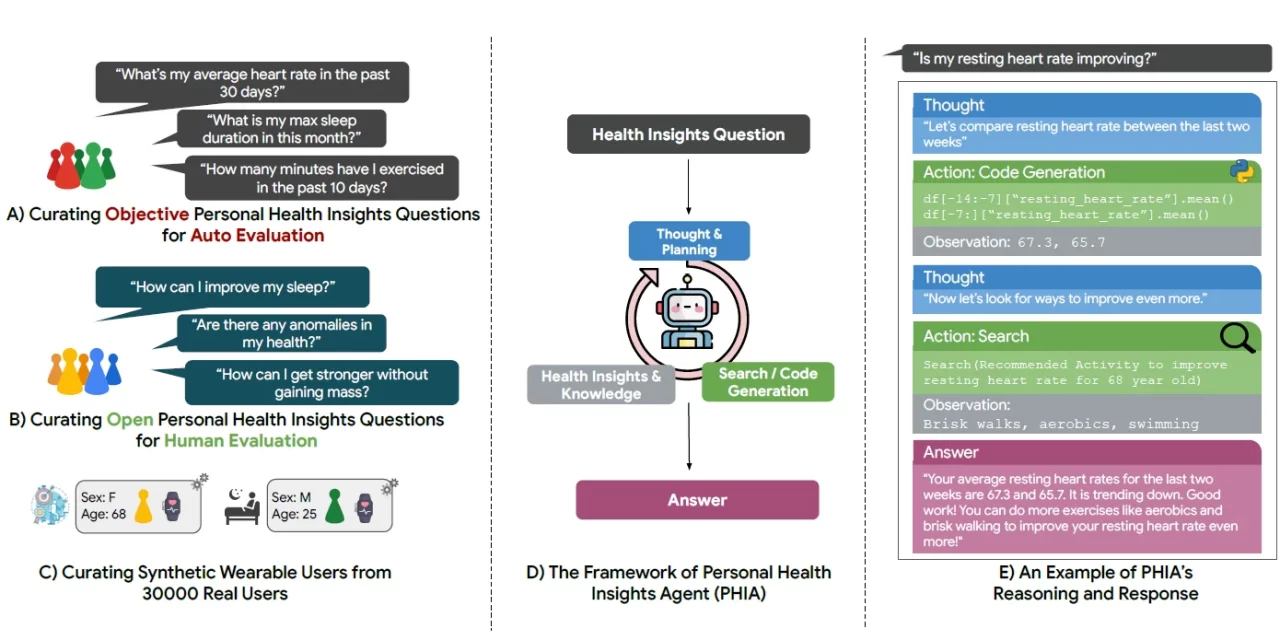
In a groundbreaking development, a team of Google engineers and researchers has introduced the Personal Health Insights Agent (PHIA), a large language model (LLM) agent system designed to analyze and infer behavioral health data from wearable health trackers. This innovative tool, detailed in a recent study on the arXiv preprint server, leverages advanced code generation methods and information retrieval tools to offer personalized health insights.
The Growing Importance of Wearable Health Data
Wearable health technology has revolutionized how we monitor health outside clinical settings, providing continuous, multi-dimensional data on behavior and physiology. These devices track everything from sleep patterns to physical activity levels, offering a wealth of information that can help promote healthier lifestyles and reduce disease risks. However, the vast amount of data collected by these devices often lacks clinical interpretation, leaving users unsure how to translate this information into actionable wellness strategies.
Enter PHIA: An Advanced AI Health Companion
PHIA represents a significant leap forward in addressing this gap. It utilizes the ReAct agent framework, enabling it to autonomously perform functions and integrate observations into its decision-making processes. By combining advanced code generation, integrated web search capabilities, and dynamic interaction, PHIA is designed to answer a wide range of health-related questions with precision and depth.
Rigorous Evaluation and Impressive Results
The study involved an extensive evaluation process, including a human assessment by 19 annotators of over 6,000 model responses and an automatic evaluation of twice that number. The results were promising: PHIA demonstrated superior reasoning on longitudinal behavioral health data and provided deep insights into health interpretations, outperforming traditional text-only numerical reasoning tools and other LLM-based non-agent tools.
Two baseline models—code generation and numerical reasoning—were used to benchmark PHIA’s performance. The evaluation included 12 expert human annotators who assessed PHIA’s responses to open-ended queries about fitness and sleep patterns. They evaluated the quality of reasoning, the relevance of data used, the accuracy of question interpretation, the incorporation of domain knowledge, logical correctness, the exclusion of harmful content, and the clarity of communication.
Superior Performance Across Metrics
PHIA’s iterative capabilities and interactive use of reasoning and planning tools allowed it to excel in providing objective insights on personal health queries. Compared to the code generation and numerical reasoning baselines, PHIA’s performance was 14% and 290% greater, respectively. For complex, open-ended queries, expert annotators reported significantly better performance from PHIA in health insight reasoning and interactive analysis.
Furthermore, PHIA provided accurate answers to over 84% of factual numerical queries and more than 83% of open-ended questions that were crowd-sourced. This high level of accuracy underscores PHIA’s potential to help individuals interpret their wearable health data and develop personalized health regimens.
Future Implications
The study concludes that PHIA, as an LLM-based agent, outperforms established baselines in using tools and iterative reasoning to analyze wearable health data. With the integration of advanced LLM models and medical domain knowledge, the potential applications of LLM-based agents like PHIA in personal health are vast. This innovation could lead to more accessible and accurate health insights, empowering users to make informed decisions about their well-being.
Google’s introduction of PHIA marks a significant step towards harnessing the power of AI to interpret wearable health data, potentially transforming how individuals manage their health and wellness.