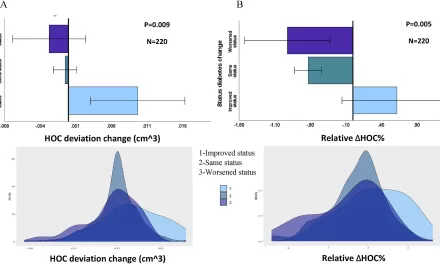
The World Health Organization (WHO) has flagged a significant rise in Mpox cases worldwide, recording 906 new instances across 26 countries in November. This surge reflects a concerning 26% increase compared to October, as outlined in the WHO’s latest monthly update.
Most of the reported cases in November emerged from the Americas (34%) and the European Region (29%). Within the Americas, the United States reported nearly 300 cases, while Portugal reported 128 new cases in Europe. Asia observed an increase in cases in Singapore, contrasting with a decline in cases reported from China.
While Africa reported a slight decrease, irregular reporting and a high number of suspected cases in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) complicate the interpretation of trends in the region, according to the WHO.
The WHO emphasized the unpredictable geographical spread of cases, cautioning against definitive regional predictions. The persistent high number of global cases indicates an ongoing outbreak, highlighting the virus’s ability to target susceptible populations.
The organization noted no substantial changes in the disease’s epidemiology. From January 1, 2022, to November 30, 2023, a total of 92,783 laboratory-confirmed Mpox cases, including 171 deaths, have been reported across 116 countries. Sexual encounters remain the most prevalent mode of transmission, constituting 83.1% of reported transmission events.
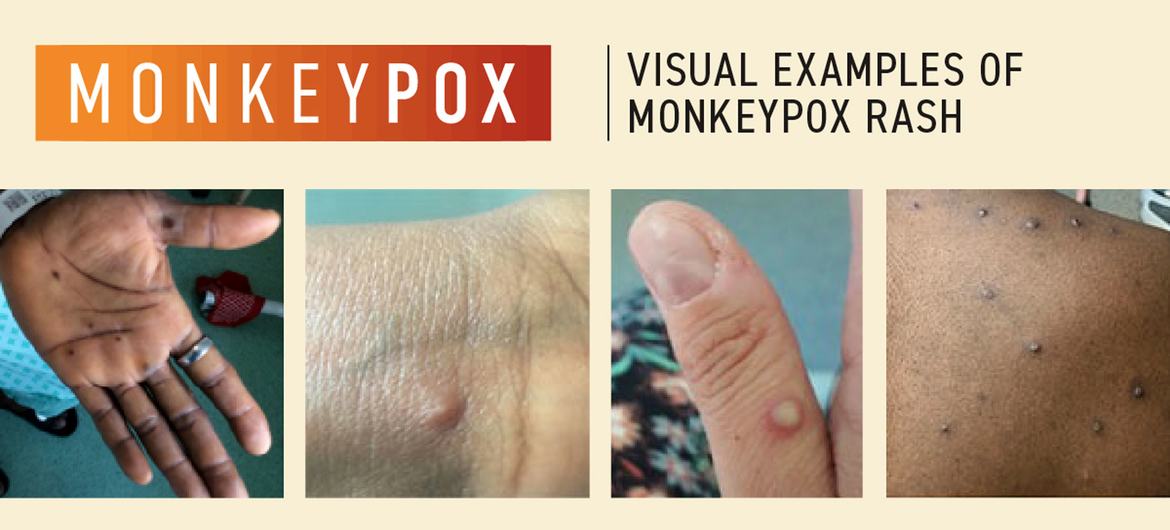
Over the last six months, 97.1% of new cases reported sexual contact, maintaining a consistent pattern. The most commonly reported symptoms include any rash (89.9% of cases), fever (58.4%), and systemic or genital rashes (54.3% and 50.2%, respectively).
The WHO’s observations underline the urgency to address this continuing outbreak and emphasize the persistence of Mpox as a global health concern.