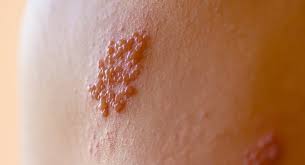
Genital herpes infections, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), impose a staggering economic burden globally, amounting to billions of dollars in healthcare costs and productivity losses. This revelation comes from the first comprehensive global estimates of the economic impact of genital herpes infections, detailed in a study published in BMC Global and Public Health on July 1st.
Led by Nathorn Chaiyakunapruk, PharmD, PhD, and Haeseon Lee, PharmD, of the University of Utah Health’s College of Pharmacy, in collaboration with the World Health Organization and other academic institutions, the research provides a detailed analysis of the economic costs associated with genital herpes infections worldwide.
Genital herpes is primarily caused by HSV-2, transmitted through sexual contact, while HSV-1, typically causing oral herpes or cold sores, can also lead to genital infections through oral-genital contact. The study reveals that approximately 13% of the global population aged 15–49 years lives with HSV-2 infection, highlighting its widespread impact.
Beyond the physical discomfort of sores and blisters, HSV infections can lead to severe complications, including an increased risk of HIV transmission and rare instances of mother-to-child transmission during childbirth. These complications necessitate significant healthcare expenditures and contribute to substantial productivity losses due to illness and stigma associated with the infection.
The study underscores the urgent need for enhanced investment in prevention strategies, including the development of effective vaccines against HSV. Such measures not only have the potential to reduce the economic burden associated with genital herpes infections but also to alleviate the personal and societal toll inflicted by this common viral infection.
The findings serve as a critical call to action for healthcare policymakers and researchers to prioritize the development and implementation of preventive measures that can mitigate the global impact of genital herpes infections on both health and economic well-being.
For more details, refer to the study published in BMC Global and Public Health under the reference: Chaiyakunapruk, N., et al. (2024) Estimated global and regional economic burden of genital herpes simplex virus infection among 15–49 year-olds in 2016. BMC Global Public Health. doi.org/10.1186/s44263-024-00053-6.
Source: University of Utah Health