The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare has surged, with nearly 900 AI tools receiving approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Despite the plethora of options, the real challenge lies in discerning which tools genuinely enhance patient care and reduce costs. Nigam Shah, PhD, chief data scientist for Stanford Health Care, emphasizes that FDA approval does not inherently equate to value. “You want AI that improves care while lowering costs,” says Shah, highlighting the importance of assessing AI tools’ actual impact on healthcare systems.
To navigate the crowded AI landscape, Shah and other experts have identified the top five AI tools currently making significant impacts in hospitals. These tools were chosen based on expert recommendations and recognition from organizations like the Coalition for Health AI and the Health AI Partnership.
1. LumineticsCore
What it is: An AI tool for diagnosing diabetic retinopathy.
Who it’s for: Optometrists, ophthalmologists, primary care physicians, and endocrinology clinics.
Diabetic retinopathy, a leading cause of blindness in the United States, often goes undetected. Traditional eye exams can take over a week for results, discouraging follow-up care. LumineticsCore, an FDA-approved tool, addresses this by providing immediate diagnosis using retinal images. The AI-based algorithm detects and analyzes biomarkers, offering a diagnosis during the same appointment. Patients diagnosed by LumineticsCore are three times more likely to follow up with an ophthalmologist, enhancing the quality of care significantly. Jennifer Goldsack, CEO of DiMe, notes that the company assumes full liability, reducing provider risk, and a billing code allows for private insurance reimbursement.
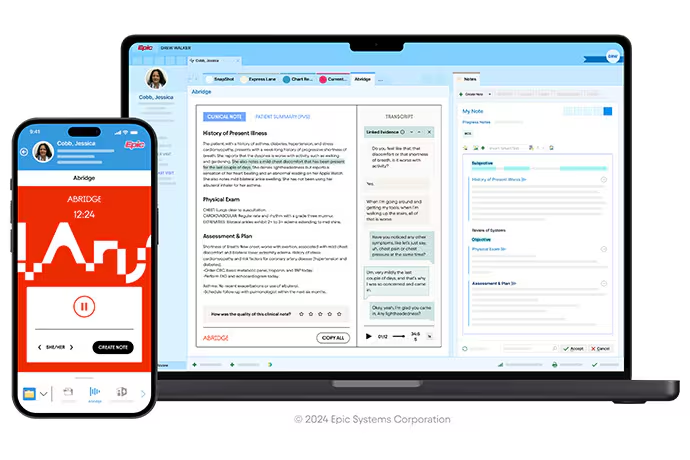
2. Abridge
What it is: An ambient listening tool for clinical notes.
Who it’s for: Physicians in any specialty aiming to reduce administrative burden.
Abridge is revolutionizing clinical documentation by enabling voice-based note-taking. Originating from the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Abridge records patient interactions, transcribes them in real-time, and uses AI to draft clinical notes. These notes are then reviewed by clinicians before being added to medical records. The tool’s use of explainable AI ensures transparency by linking note content to the source transcript. Abridge, compatible with electronic health record systems like Epic, is already in use at major healthcare centers, including Emory Healthcare and Yale New Haven Health. The tool saves significant time and reduces physician burnout, with an estimated annual savings of 85,000 hours and $1.7 million in physician turnover for a 200-physician hospital system.
3. Woebot
What it is: A conversational mental health app using machine learning.
Who it’s for: Primary care physicians and mental health specialists.
With the rising demand for mental health services, Woebot offers on-demand cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) through a conversational app. Available to patients of partner healthcare institutions, Woebot has received the FDA’s breakthrough device designation. The app provides pre-written responses crafted by clinicians, delivering reliable, therapeutic interactions. Virtua Health prescribes Woebot to patients with mild to moderate depression and anxiety, and the app’s convenience and effectiveness have made it popular among users. More than 80% of patients report a positive experience, with interactions typically lasting only 7 minutes. Woebot’s success has prompted interest from insurers, which could lead to reimbursement options.
4. VBrain
What it is: An AI-assisted brain tumor auto-contouring tool.
Who it’s for: Radiation oncologists.
VBrain, developed by Vysioneer, streamlines the process of tumor contouring for radiation therapy. This FDA-approved tool uses a deep learning algorithm to identify and contour brain tumors, including metastasis, meningioma, and acoustic neuroma. VBrain significantly reduces the time required for contouring, completing the task 30% faster than manual methods with a 12% improvement in accuracy. Stanford researchers have validated VBrain’s effectiveness in a study involving 100 patients. By automating a large portion of the contouring process, VBrain allows oncologists to focus more on patient care and less on tedious manual tasks.
5. GI Genius
What it is: An AI tool for detecting polyps during colonoscopy.
Who it’s for: Gastroenterologists and endoscopists.
GI Genius by Medtronic enhances the accuracy of colonoscopies by identifying polyps in real-time. Integrated with existing endoscopy equipment, the AI tool displays suspected polyps on the monitor, aiding endoscopists in their detection efforts. In clinical studies, GI Genius increased the adenoma detection rate (ADR) by over 14%, with each 1% increase in ADR reducing colorectal cancer risk by 3%. The tool also generates immediate reports post-endoscopy, streamlining the documentation process. By acting as a “second set of eyes,” GI Genius improves diagnostic accuracy and efficiency, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes.
These AI tools represent a promising future for healthcare, offering innovative solutions to improve patient care while addressing systemic challenges like physician shortages and increasing demand for services. As AI technology continues to evolve, the potential for even greater advancements in healthcare remains vast.