- US FDA Press Release
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration today approved Vyvgart (efgartigimod) for the treatment of generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adults who test positive for the anti-acetylcholine receptor (AChR) antibody.
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune, neuromuscular disease that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles (also called voluntary muscles) that worsens after periods of activity and improves after periods of rest. Myasthenia gravis affects voluntary muscles, especially those that are responsible for controlling the eyes, face, mouth, throat, and limbs. In myasthenia gravis, the immune system produces AChR antibodies that interfere with communication between nerves and muscles, resulting in weakness. Severe attacks of weakness can cause breathing and swallowing problems that can be life-threatening.
“There are significant unmet medical needs for people living with myasthenia gravis, as with many other rare diseases,” said Billy Dunn, M.D., director of the Office of Neuroscience in the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. “Today’s approval is an important step in providing a novel therapy option for patients and underscores the agency’s commitment to help make new treatment options available for people living with rare diseases.”
Vyvgart is the first approval of a new class of medication. It is an antibody fragment that binds to the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), preventing FcRn from recycling immunoglobulin G (IgG) back into the blood. The medication causes a reduction in overall levels of IgG, including the abnormal AChR antibodies that are present in myasthenia gravis.
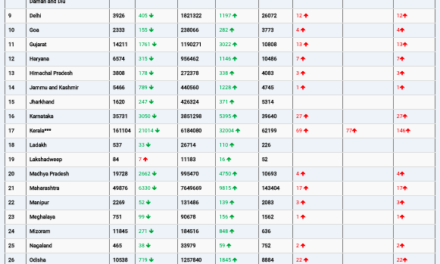
The safety and efficacy of Vyvgart were evaluated in a 26-week clinical study of 167 patients with myasthenia gravis who were randomized to receive either Vyvgart or placebo. The study showed that more patients with myasthenia gravis with antibodies responded to treatment during the first cycle of Vyvgart (68%) compared to those who received placebo (30%) on a measure that assesses the impact of myasthenia gravis on daily function. More patients receiving Vyvgart also demonstrated response on a measure of muscle weakness compared to placebo.
The most common side effects associated with the use of Vyvgart include respiratory tract infections, headache, and urinary tract infections. As Vyvgart causes a reduction in IgG levels, the risk of infections may increase. Hypersensitivity reactions such as eyelid swelling, shortness of breath, and rash have occurred. If a hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue the infusion and institute appropriate therapy. Patients using Vyvgart should monitor for signs and symptoms of infections during treatment. Health care professionals should administer appropriate treatment and consider delaying the administration of Vyvgart to patients with an active infection until the infection is resolved.
The FDA granted this application Fast Track and Orphan Drug designations. The FDA granted the approval of Vyvgart to argenx BV.