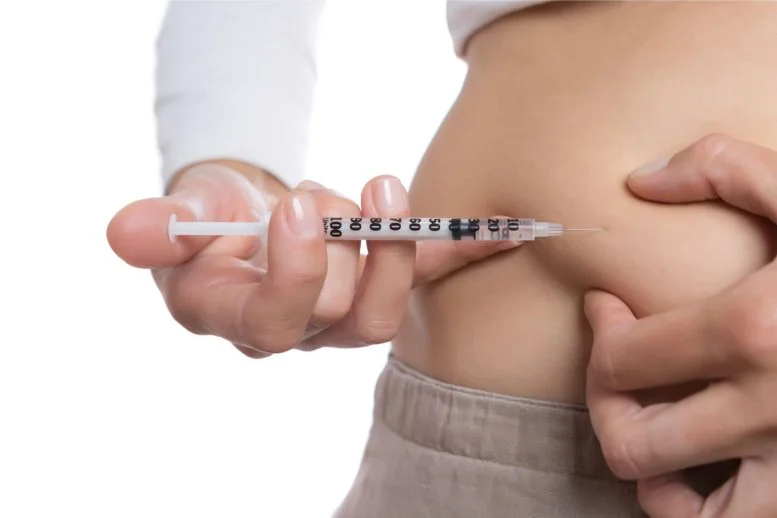
Washington, D.C. – The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has granted approval for Sanofi’s Merilog (insulin-aspart-szjj), a biosimilar to Novolog (insulin aspart), for the treatment of diabetes in both adults and children. This approval marks a significant advancement in the availability of affordable insulin options for patients.
According to Dr. Peter Stein, Director of the Office of New Drugs at the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, the approval underscores the agency’s ongoing commitment to expanding access to essential medications. “Increasing access to safe, effective, and high-quality medications at potentially lower costs remains a continued priority for the FDA,” Stein stated.
Merilog is the first rapid-acting biosimilar human analog insulin to receive FDA approval. Since March 2020, the FDA has regulated insulin and other biological products as biosimilars, ensuring they maintain high similarity with no clinically meaningful differences from their reference products. This allows for interchangeability at the pharmacy level without requiring a new prescription from healthcare providers.
The FDA has previously approved two long-acting insulin biosimilars: Mylan Pharmaceuticals’ Semglee in June 2020 and Lilly’s glargine biosimilar, Rezvoglar, in December 2021. Prior to the establishment of the biosimilar category for insulin, the agency had approved Sanofi’s short-acting insulin lispro follow-on, Admelog, in 2017, and Eli Lilly’s authorized generic Insulin Lispro in 2019. The long-acting follow-on Basaglar (Lilly) received approval in 2015.
Merilog will be available in two forms: a 3 mL single-patient-use prefilled pen and a 10 mL multiple-dose vial. It is intended to be administered subcutaneously within 5-10 minutes before a meal, with dosing individualized based on the patient’s needs.
As with other rapid-acting insulin analogs, Merilog carries the risk of serious side effects, including hypoglycemia, severe allergic reactions, and hypokalemia. Additional common side effects include injection-site reactions, itching, rash, lipodystrophy, weight gain, and swelling of the hands and feet.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Patients should consult their healthcare provider before making any changes to their diabetes treatment regimen.