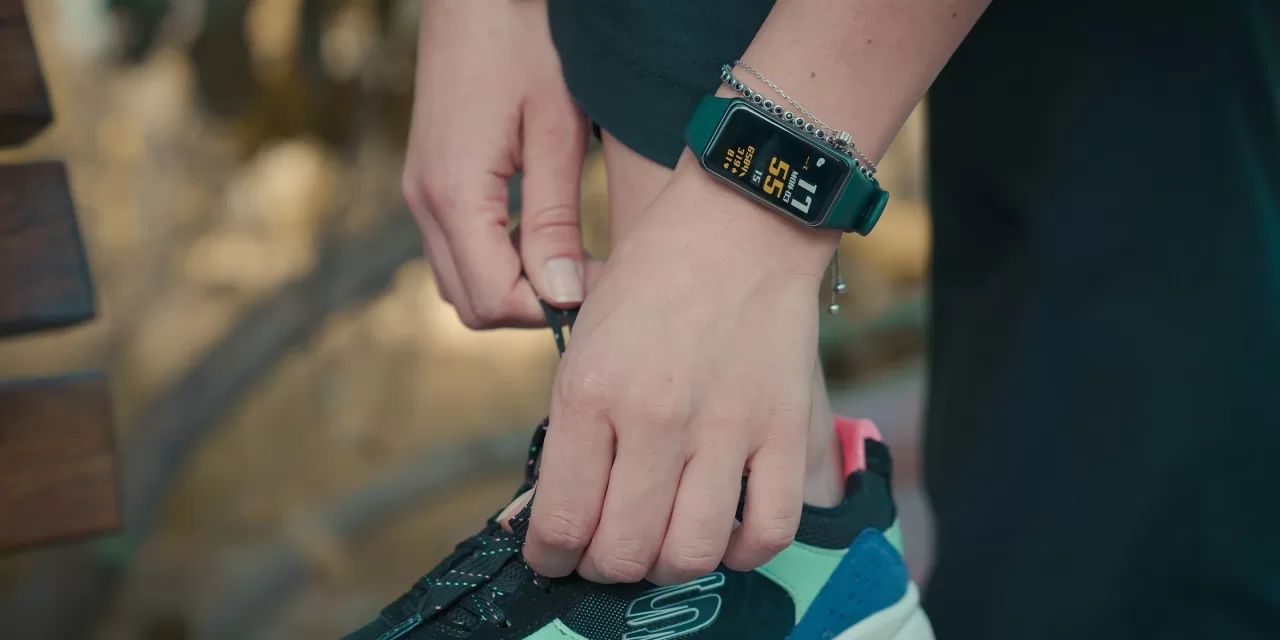
Preventive health technologies like wrist-worn activity trackers and health and fitness apps have surged in popularity, offering consumers innovative ways to monitor and enhance their well-being. However, new research published in the Journal of Consumer Affairs highlights the complex relationship between these tools and users’ mental and physical health. According to the study, consumer engagement with these technologies can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on individual usage patterns.
The study, led by Lisa Baiwir, a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Liège, Belgium, involved 30 in-depth interviews with users of preventive health technologies. The research sought to explore how and why people engage with these devices and apps, uncovering various motivations. Users reported diverse health goals, such as weight loss, performance improvement, or building healthy routines. Others used the devices to track enjoyable activities, or simply to monitor data as part of a broader lifestyle choice.
Interestingly, the study identified different “engagement trajectories” among users. Some experienced heightened engagement initially but later reached a stable level of interaction. Others lost interest after an initial spike in activity, while a third group became obsessive, leading to over-engagement with the technology. Some users even reported fluctuating cycles of engagement, moving between high and low usage periods over time.
The implications of these trajectories were significant. While many found that the technologies helped them establish and maintain healthy routines, others fell into compulsive usage patterns. This over-reliance on the devices led to what researchers termed “ill-being,” where users experienced heightened stress, anxiety, and feelings of failure when they couldn’t meet self-imposed goals or metrics set by the apps.
“As preventive health technologies become more integrated into our daily lives, it’s crucial to understand the factors that lead to over-engagement and ill-being, so that designers of health apps can mitigate these risks,” Baiwir noted.
For developers of health tech, the study provides valuable insights. Understanding the balance between promoting healthy habits and preventing overuse is critical as these tools become more sophisticated. Developers may need to integrate features that promote moderation, encouraging users to step back when their engagement becomes compulsive.
The study sheds light on the double-edged sword that these technologies can represent. While they offer promising tools for enhancing well-being, they can also exacerbate stress and unhealthy habits if used obsessively. As the field of preventive health technology evolves, the challenge will be in designing systems that maximize benefits while minimizing potential harm to consumers.
Reference:
Lisa Baiwir et al, Consumer engagement with preventive health technologies: A double-edged sword for consumer wellbeing, Journal of Consumer Affairs (2024). DOI: 10.1111/joca.12603