Situation at a Glance
Description of the Situation
On 5 September 2023, the Ministry of Health notified WHO of the current diphtheria outbreak in Guinea. On 4 July 2023, two children aged 2 and 4 years, attended the otolaryngology department of the Siguiri prefectural hospital in the Kankan region of Guinea, for similar symptoms (dyspnea, dysphasia, fever, cough). They were hospitalized for tonsillitis and respiratory infection and received antibiotic treatment before being referred to the Kankan regional hospital for additional care.
Since 4 July and as of 13 October 2023, 538 cases have been reported, including 18 confirmed cases. In total, 58 deaths including 13 among confirmed cases were registered (case fatality rate (CFR) among all cases, 11%)., and 461 contacts are being followed up. Of the cases reported, 62% are female. The 1-4 years age group, with 445 cases, accounted for the largest proportion of reported cases, 82%, followed by the 5-9 years age group, with 5% and 5% for the 10 years and above age group. Children under the age of 12 months make up 7% of reported cases. None of the 538 cases were vaccinated.
Kankan Region is divided into five prefectures and only the Kérouané prefecture has not reported any cases to date.
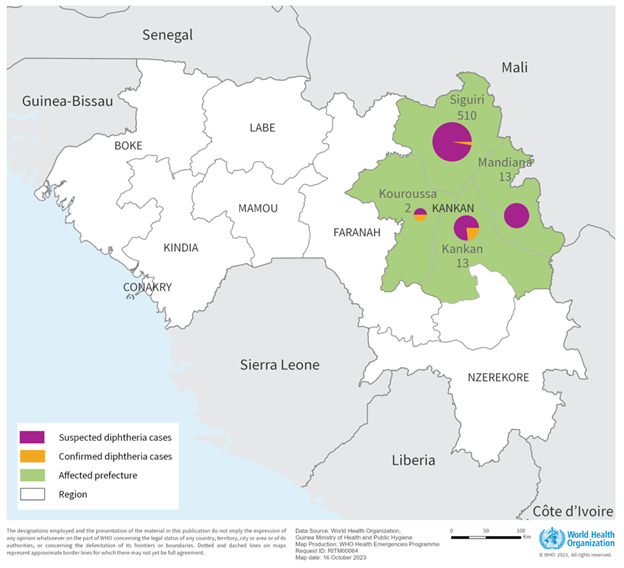
The prefecture of Siguiri is the most affected, with 510 cases (95%). Of the 363 patients admitted to the treatment centers in Siguiri, 37 (10%) have died.
Other prefectures reporting cases are Mandiana (13 cases), Kankan (13 cases) and Kouroussa (two cases). Of the 15 patients admitted in the treatment center in Kankan, 12 (80%) have died.
The treatment centers in the country do not have the capacity in terms of human resources and material for adequate case management. Suspected and confirmed cases were treated with Amoxicillin and Azithromycin as first line therapy. Antibiotic prophylaxis (Amoxicillin, Azithromycin) was administered to the direct contacts.
Figure 1: Distribution of diphtheria cases in Kankan region, Guinea, as of 13 October 2023
Epidemiology
Diphtheria is a highly contagious vaccine-preventable disease caused mainly by Corynebacterium diphtheria but also byCorynebacterium ulcerans. It spreads between people mainly by direct contact or through the air via respiratory droplets. The disease can affect all age groups; however, unimmunized children are most at risk.
Symptoms often come on gradually, beginning with a sore throat and fever. In severe cases, the bacteria produce a poison (toxin) that causes a thick grey or white patch at the back of throat. This can block the airways, making it hard to breathe or swallow, and also creates a barking cough. The neck may swell in part due to enlarged lymph nodes.
Treatment involves administering diphtheria antitoxin (DAT) as well as antibiotics. Vaccination against diphtheria has been effective in reducing the mortality and morbidity from diphtheria dramatically. Diphtheria is fatal in 5-10% of cases, with a higher mortality rate in young children. However, in settings with poor access to DAT, the CFR can be as high as 40%.
Public Health Response
- Guinea has strengthened epidemiological surveillance for early detection and case management.
- Daily coordination and monitoring meetings on the response activities are underway at the Regional level, led by the regional health inspector and with the support of WHO, MSF- Belgium and other partners in the region.
- Notification of all suspected cases of diphtheria, investigation initiation, and monitoring of contacts as soon as possible has been enhanced.
- Contact tracing, identification of an isolation zone at the Balato health post in the prefecture of Kouroussa and briefing of the healthcare workers on the case definition and prevention measures are ongoing.
- Case management activities such as antibiotic therapy (Amoxicillin, Azithromycin), treatment of suspected cases, antibiotic prophylaxis (Amoxicillin, Azithromycin) for the direct contacts and free case management at treatment centers with support from MSF are provided.
- Risk communication and community engagement efforts, such as raising awareness of cases in the community and identifying and briefing a communicator to raise awareness among parents of patients is ongoing.
WHO Risk Assessment
Diphtheria is a vaccine-preventable disease caused by exotoxin-producing Corynebacterium diphtheriae, transmitted from person to person through close physical and respiratory contact. It can cause infection of the nasopharynx, which may lead to breathing difficulties and death. Diphtheria is fatal in 5 – 10% of cases, with a higher mortality rate in young children. Treatment involves administering diphtheria antitoxin as well as antibiotics. Vaccination against diphtheria has reduced the mortality and morbidity of diphtheria dramatically.
The DAT supply is currently very constrained and insufficient to respond to current demands, as there is only a limited number of manufacturers and large outbreaks are being reported in different regions of the world.
The risk of diphtheria in Guinea is considered high due to the low DTP3 vaccination coverage in the affected region (36% according to the survey coverage in households, 2023) and 47% national DTP3 vaccination coverage between 2014-2022 (per WHO/UNICEF estimates), and the risk at the regional level is moderate and low at the global level. The outbreak is also characterized by high case fatality among confirmed cases. Other factors include: the over population of the Siguiri health district, which is the epicenter of this outbreak, the weakened healthcare system and several concurrent epidemics in the area.
The overpopulation of the Siguiri health prefecture, the epicenter of this epidemic, the insufficient poorly qualified health personnel, and the limited material resources of the health system weakens the response to this outbreak. In addition, the country is facing several concurrent epidemics in the area, such as pertussis, poliomyelitis, and rabies. Adding this to a context of extreme vulnerability due to mining activities, which induce significant population movement, reduce air quality, and increase the risk of natural disasters such as floods and landslides, impacting people’s health.
This emphasizes the urgent need to strengthen diphtheria vaccination coverage nationwide, especially in the epicenter and strengthen case management at hospital facilities dealing with diphtheria cases.
WHO Advice
The control of diphtheria is based on primary disease prevention by ensuring high population immunity through vaccination and secondary prevention of spread by the rapid investigation of close contacts to ensure prompt treatment of those infected.
Epidemiological surveillance ensuring early detection of diphtheria outbreaks should be in place in all countries, and all countries should have access to laboratory facilities for reliable identification of toxigenic C. diphtheriae. Adequate quantities of diphtheria antitoxin should be available nationally or regionally for the medical management of cases.
Vaccination is vital to preventing cases and outbreaks, and adequate clinical management involves administering diphtheria anti-toxin to neutralize the toxin and antibiotics reducing complications and mortality.
WHO recommends early reporting and case management of suspected diphtheria cases to initiate the timely treatment of cases and follow-up of contacts and ensure the supply of diphtheria antitoxin.
WHO advises implementing the following Infection Prevention & Control (IPC) measures in health care settings:
At screening/triage, immediately place patients with symptoms of Upper Respiratory Tract Infection (URTI) in a separate area until examined, and, if a probable case, cohorted with patients with the same diagnosis. Keep the isolation area segregated from other patient-care areas.
In addition to using standard precautions, patients with known or suspected respiratory diphtheria are placed under droplet precautions. Patients with known or suspected cutaneous diphtheria should be placed under contact precautions. Maintain one meter between patients. Keep patient care areas well- ventilated. Avoid patient movement or transport out of the isolation area. If movement is necessary out of the isolation area, have the patient use a medical mask and cover any wounds/lesions on the patient’s body.
Case management should be carried out following the WHO guidelines. In addition, high-risk populations such as young children under five years of age, school children, the elderly, close contact with diphtheria cases, and healthcare workers should be vaccinated on a priority basis. A coordinated response and community engagement can support further transmission and control of the ongoing outbreak.
Prophylactic antibiotics (penicillin or erythromycin, dependent on the isolate antibiotic sensitivity) are indicated for close contacts for seven days. If the culture is positive for toxigenic Corynebacterium spp.., the contact should be treated as a case with an antibiotic course for two weeks (DAT is not needed for asymptomatic cases or cases without a pseudo membrane).
Although travelers do not have a particular risk of diphtheria infection, it is recommended that national authorities remind travelers going to areas with diphtheria outbreaks to be appropriately vaccinated in accordance with the national vaccination scheme established in each country before travel. A booster dose is recommended if more than five years have passed since their last dose.
WHO does not recommend that any general travel or trade restrictions be applied to Guinea based on the information available for this event.
Further Information
- WHO diphtheria page: https://www.who.int/teams/health-product-policy-and-standards/standards-and-specifications/vaccine-standardization/diphtheria
- Manual for quality control of diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and combined vaccines: https://www.who.int/publications-detail-redirect/WHO-IVB-11.-11
- Diphtheria: Vaccine Preventable Diseases Surveillance Standards: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/vaccine-preventable-diseases-surveillance-standards-diphtheria
- Transmission-based precautions for the prevention and control of infections: aide-memoire: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-UHL-IHS-IPC-2022.2
- WHO. Diphtheria: Clinical management of respiratory diphtheria: https://openwho.org/courses/diphtheria-clinical-management
Citable reference: World Health Organization (18 October 2023). Disease Outbreak News; Diphtheria in Guinea. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/disease-outbreak-news/item/2023-DON492