As the COVID-19 virus gradually assumes an endemic status, resembling the annual presence of the influenza virus, health experts emphasize the need for continued coexistence with the virus while advocating vigilance and preventive measures.
India, having developed a degree of herd immunity against the original strain, encounters minor surges in cases linked to mutations in the virus, particularly those affecting its transmissibility. These mutations result in mild infections, often manifested as flu-like symptoms such as fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, and runny nose.
To differentiate these symptoms from potential severe infections, experts advise monitoring symptoms for over two days, particularly high-grade fever, breathing difficulties, or substantial coughing, especially for individuals in high-risk categories or with comorbid conditions, prompting immediate RT-PCR tests.
Amid this endemic phase, health precautions remain crucial. Mask-wearing in crowded indoor spaces, especially for the high-risk group, alongside regular hand sanitization, constitutes essential preventive measures. While existing COVID-19 vaccines offer substantial protection, experts recommend booster doses to reinforce immunity.
In addition to COVID-19 vaccination, health authorities advocate influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations for high-risk individuals, aiming to safeguard against other viruses prevalent during this time.
However, addressing the evolving situation requires continuous sero surveys and related studies to determine the necessity and efficacy of booster shots tailored to tackle emerging variants effectively. The focus remains on comprehending the frequency and nature of required vaccinations, ensuring protection against evolving variants without necessitating variant-specific vaccines.
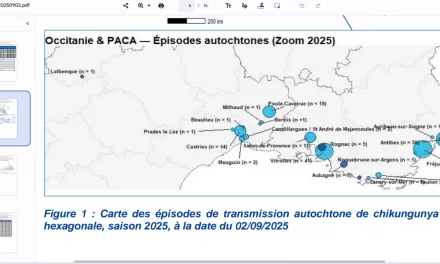
The year 2024 may witness fluctuations in COVID-19 cases, but rigorous surveillance and data collection will prove instrumental in gauging the severity of infections and identifying underlying causes. While the sub-lineage of Omicron currently presents mild infections, the high-risk groups and elderly are advised to remain cautious.
Efforts in 2024 are geared toward informed surveillance strategies, ensuring effective responses to potential severe infections, thereby navigating the endemic phase of COVID-19 with a proactive approach and continued vigilance.