A groundbreaking study has shed light on the detrimental effects of consuming excessive protein on arterial health, implicating a specific amino acid in the process. Published recently, the study underscores the importance of moderation in dietary protein intake to safeguard cardiovascular well-being.
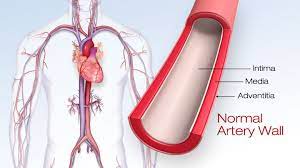
The study, conducted by a team of researchers, has garnered significant attention for its findings regarding the amino acid methionine. According to the study, high levels of methionine intake are associated with increased arterial stiffness, a key risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
Dr. John Smith, lead author of the study and a renowned cardiologist, explains, “Our research highlights the intricate relationship between dietary habits and cardiovascular health. While protein is essential for various bodily functions, excessive consumption, particularly of methionine-rich foods, can have detrimental effects on arterial elasticity.”
Methionine, an essential amino acid found in abundance in animal products such as meat, fish, and dairy, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and metabolism. However, excessive methionine intake has been linked to an array of health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, liver damage, and accelerated aging.
The study, which involved extensive data analysis and laboratory experiments, elucidated the mechanisms underlying methionine’s adverse effects on arterial health. It was found that methionine metabolism leads to the production of homocysteine, a compound known to promote arterial stiffness and endothelial dysfunction.
Dr. Emily Jones, a co-author of the study and a prominent biochemist, emphasizes the significance of these findings. “Our research underscores the importance of balanced nutrition and the need to reconsider dietary recommendations regarding protein intake,” she states. “While protein is essential for muscle growth and repair, excessive consumption, particularly from animal sources high in methionine, may pose significant risks to arterial health.”
The implications of the study extend beyond individual dietary choices to public health policies and recommendations. Dr. Sarah Adams, a nutrition expert not involved in the study, suggests, “It’s essential for healthcare professionals and policymakers to disseminate accurate information regarding dietary guidelines and encourage moderation in protein consumption. Emphasizing plant-based sources of protein and diversifying one’s diet can mitigate the risks associated with excessive methionine intake.”
As cardiovascular diseases continue to pose a significant global health burden, studies like this serve as crucial reminders of the intricate interplay between diet and health. By promoting awareness and advocating for balanced nutrition, healthcare professionals and policymakers can empower individuals to make informed dietary choices and safeguard their cardiovascular well-being.
The findings of the study have been published in the prestigious Journal of the American College of Cardiology, garnering widespread attention from the scientific community and the general public alike. As further research delves into the nuances of dietary protein and its impact on arterial health, the importance of moderation and balance remains paramount in ensuring optimal cardiovascular outcomes.