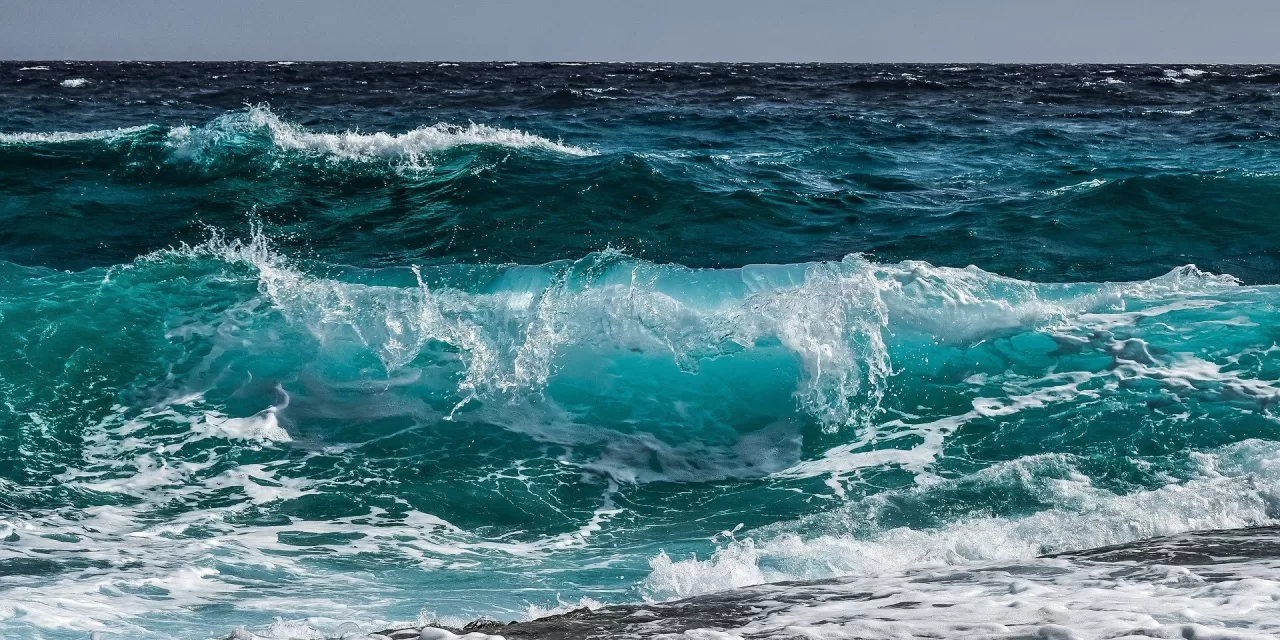
Have you ever found yourself gazing out at the sea and felt the world around you become smaller? Or perhaps you’ve swum in its waters, experiencing a sense of timelessness as the noise of daily life fades away into a distant hum? Whether it’s marveling at the sun setting on the horizon or feeling awe in the face of such vastness, the ocean has a unique ability to calm our minds and restore our spirits.
These feelings, often described as a sense of awe, have long intrigued psychologists and researchers. Interestingly, the benefits of being near water are not just emotional—they are deeply tied to our physical and mental well-being. This phenomenon, known as “blue health,” refers to the positive effects that oceans, rivers, and other bodies of water have on our health.
The Science Behind Blue Health
Scientific studies have consistently shown that spending time near water improves our health in a variety of ways. One of the key reasons for this is that being near natural water sources often encourages physical activity, such as walking along the shore, swimming, or engaging in water sports. This increased physical movement has obvious health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health and muscle tone.
However, the benefits of blue spaces extend beyond physical health. Natural environments, particularly those involving water, are restorative to our mental well-being. Research indicates that spending time in these “blue spaces” reduces stress, enhances mood, and boosts feelings of relaxation. Simply observing or interacting with water can help us disconnect from the overwhelming distractions of daily life, giving our minds the space to recover and reset.
Moreover, these benefits are not only emotional. Being near water can also improve the quality of the surrounding environment, contributing to an overall better sense of well-being. Cleaner air, soothing sounds, and the calming sight of water can all have indirect, yet significant, health benefits.
A Biological Connection to the Sea
The connection between humans and the sea is not just cultural or emotional; it is biological. Life on Earth began in the oceans, and our bodies share many similarities with this aquatic environment. For instance, our sweat and tears have the same salty composition as seawater, which serves as a reminder of our deep connection to the ocean. This link is further explored by the biophilia hypothesis, which suggests that humans have an innate attraction to natural environments like the sea because of their biological origins.
Along with biophilia, two other theories help explain why we are drawn to water: psychophysiological stress recovery and attention restoration theory. Together, these theories demonstrate that our attraction to the sea is not only natural but deeply beneficial to our health.
Restoration and Mental Well-Being
The sea offers more than just a chance for physical relaxation; it provides a mental escape. Whether it’s walking on the beach, sailing across the water, or simply sitting and gazing at the horizon, time spent by the ocean helps clear our minds and ease our mental struggles. The sense of restoration we experience in these moments helps us to find mental clarity and focus, something many of us struggle to achieve in the chaos of modern life.
This restoration is particularly important in today’s fast-paced world, where chronic stress, anxiety, and information overload are common. Blue health provides a respite—a moment of peace that helps restore balance and perspective, allowing us to recharge both mentally and physically.
Sea, Sport, and Disability
The benefits of the sea extend to people of all abilities. For individuals with disabilities or those recovering from injuries that make movement difficult, the water offers a unique form of therapy and freedom. The buoyancy of the sea provides a gentle, supportive environment where people can experience a sense of autonomy and relaxation that may be hard to find on land.
Water sports, particularly those in the sea, are gaining recognition for their therapeutic benefits. From adaptive sailboats and diving therapy to yoga and stand-up paddleboarding, there are numerous ways for people with disabilities to engage with the water and experience its transformative effects. These activities not only promote physical well-being but also encourage emotional healing and a deeper connection to nature.
The Sea Belongs to Everyone
The sea’s power to heal is universal. Regardless of age, ability, or background, everyone can benefit from the calming, restorative qualities of blue spaces. By making water-based activities accessible to all, we can ensure that everyone has the opportunity to experience the freedom, relaxation, and connection that the sea offers.
As we continue to explore and understand the profound effects of blue health, it is clear that the sea’s power to enhance our physical and mental well-being is something we all can embrace. Whether we’re dipping our toes in the sand, diving into the waves, or simply admiring its vastness, the ocean reminds us of our shared connection to nature—and the immense, transformative power it holds for us all.