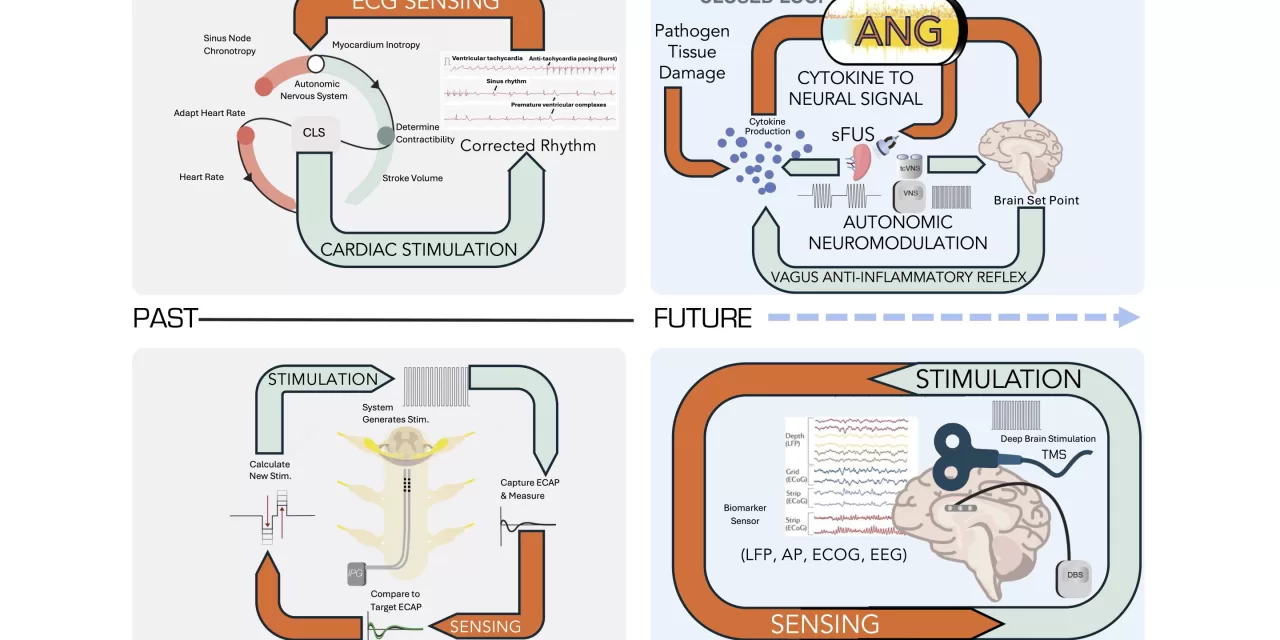
San Diego, CA – From ancient Egyptian treatments to modern pacemakers, bioelectronic medicine, which utilizes electrical signals to treat diseases, has steadily evolved. Now, new research led by Imanuel Lerman, a renowned scientist at UC San Diego, provides a roadmap for the next generation of this promising field.
Beyond Pacemakers:
While pacemakers remain a cornerstone, bioelectronic medicine has expanded significantly. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease, spinal cord stimulation for back pain, and vagus nerve stimulation for epilepsy are just a few examples of its successful applications.
Non-Invasive Approaches:
The rise of non-invasive techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) has further broadened the field’s reach. TMS, initially approved for depression, now addresses migraines, OCD, and even smoking cessation.
Key Advantages:
Lerman emphasizes the advantages of non-invasive neuromodulation:
- Reduced Risk: Avoiding surgeries minimizes potential complications.
- Scalability: Devices are easily transportable and don’t require refrigeration like pharmaceuticals.
- Body-Centric Approach: Leveraging the body’s own systems to reduce inflammation offers a more natural approach.
Closed-Loop Systems:
A key focus is the development of “closed-loop” systems. These systems, combining bioelectronic devices with sensors, can continuously monitor a patient’s condition and adjust treatment accordingly, offering truly personalized medicine.
Diagnostic Potential:
Bioelectronic medicine may revolutionize disease diagnosis. Research suggests that the body produces unique electrical responses to infections. By analyzing these patterns, doctors could identify the specific pathogen and tailor treatment accordingly.
Mental Health Applications:
Given the strong link between inflammation and mental health conditions like PTSD and depression, bioelectronic medicine holds immense promise. Assessing brain inflammation could help diagnose and treat these disorders with greater precision.
Looking Ahead:
While challenges remain, Lerman and his team believe that bioelectronic medicine has the potential to transform healthcare. By embracing non-invasive techniques, closed-loop systems, and innovative diagnostic approaches, this field is poised to usher in a new era of personalized and effective treatments.
Disclaimer: This is a simplified version of the research findings. For a comprehensive understanding, refer to the original research paper in Bioelectronic Medicine.