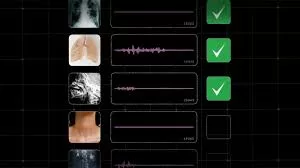
Revolutionizing healthcare through sound, Google Research introduces HeAR, a bioacoustic AI model that offers new possibilities in early disease detection, with a focus on conditions like tuberculosis and COPD.
In the evolving landscape of medical diagnostics, sound has emerged as a powerful and untapped resource for detecting health conditions. Google Research has taken a significant step forward with the introduction of Health Acoustic Representations (HeAR), an AI model designed to analyze the subtle clues hidden within the sounds our bodies produce—whether it be a cough, breath, or even speech. This innovative approach holds the potential to revolutionize the screening, diagnosis, and management of various diseases, including tuberculosis (TB) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
HeAR is a bioacoustic foundation model that was trained on a vast dataset comprising 300 million pieces of audio data, with 100 million of those focused specifically on cough sounds. The model is designed to discern patterns within health-related acoustic data, making it a powerful tool for medical audio analysis. The Google Research team has reported that HeAR outperforms other models in a wide range of tasks, particularly in generalizing across different microphone types, highlighting its superior ability to capture meaningful health signals.
One of the key advantages of HeAR is its efficiency in training new models with less data—a crucial benefit in healthcare research where data scarcity is often a challenge. By providing a robust foundation, HeAR enables researchers to develop custom bioacoustic models more quickly and with fewer resources, potentially accelerating breakthroughs in early disease detection and monitoring.
In India, Salcit Technologies, a respiratory healthcare company, has already begun exploring the potential of HeAR in their efforts to combat TB. Their product, Swaasa®, uses AI to analyze cough sounds and assess lung health. With the integration of HeAR, Swaasa® aims to enhance its capabilities in early TB detection, particularly in underserved areas where access to healthcare services is limited. By leveraging AI-driven acoustic analysis, Salcit Technologies is working to bridge gaps in healthcare accessibility, affordability, and scalability, bringing life-saving diagnostics to a broader population.
“Every missed case of tuberculosis is a tragedy; every late diagnosis, a heartbreak,” said Sujay Kakarmath, a product manager at Google Research. “Acoustic biomarkers offer the potential to rewrite this narrative. I am deeply grateful for the role HeAR can play in this transformative journey.”
The importance of this approach is further underscored by support from international organizations such as The Stop TB Partnership, which aims to end TB by 2030. Zhi Zhen Qin, a digital health specialist with the partnership, highlighted the potential impact of AI-powered acoustic analysis on TB screening and detection, describing HeAR as a low-impact, accessible tool that could benefit those most in need.
As HeAR continues to make strides in the field of acoustic health research, its potential applications extend beyond TB and respiratory diseases. Google Research envisions a future where diagnostic tools and monitoring solutions are developed for a variety of health conditions, ultimately improving outcomes for communities around the world. Researchers interested in exploring HeAR can request access to the model’s API, opening the door to further innovation in this exciting field of healthcare technology.
Through HeAR, Google Research is not only advancing scientific knowledge but also paving the way for more inclusive and accessible healthcare solutions, ensuring that even the most subtle sounds can be harnessed to save lives.