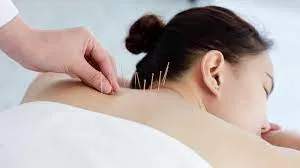
A new study published in BMJ Open suggests that acupuncture could be a potential ally in reducing the heightened risk of stroke associated with rheumatoid arthritis, offering hope for improved cardiovascular health among this patient population.
Rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disorder, not only affects the joints but also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. Seeking to explore whether acupuncture could mitigate this risk, researchers conducted a comparative study drawing on national medical records from the Registry for Catastrophic Illness Patients Database (RCIPD).
The study included 47,809 adults newly diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis between 1997 and 2010. Among them, 23,226 patients with complete data were analyzed, with 12,266 receiving acupuncture treatment following their diagnosis.
The findings revealed a significant reduction in the risk of ischaemic stroke—a stroke caused by a blood clot in the brain—among the acupuncture group compared to those who did not receive acupuncture treatment. Remarkably, this effect was observed independently of factors such as age, sex, medication use, and co-existing conditions.
Lead researcher Professor Akiyoshi Saitoh and his team found that those treated with acupuncture had a 43% lower risk of ischaemic stroke. While the exact mechanism behind this protective effect remains to be fully elucidated, the researchers hypothesize that acupuncture may reduce levels of pro-inflammatory proteins in the body, thus lowering the risk of cardiovascular diseases associated with systemic inflammation.
Although this study is observational and cannot establish a cause-and-effect relationship, the promising findings suggest that acupuncture could serve as a complementary therapy for rheumatoid arthritis patients, potentially improving their cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of stroke.
In their conclusion, the researchers emphasize the need for further research to better understand the mechanisms underlying acupuncture’s effects and to explore its potential as a therapeutic intervention for reducing stroke risk in rheumatoid arthritis patients.
As we continue to uncover the benefits of acupuncture in various health conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis, the integration of this traditional practice into mainstream healthcare offers new avenues for enhancing patient outcomes and improving quality of life.
The full study, titled “Effect of acupuncture on ischaemic stroke in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide propensity score-matched study,” can be found in BMJ Open.