March 2, 2025 – Researchers have identified a gene, EDA2R, that plays a significant role in driving age-related inflammation and degeneration, potentially opening new avenues for therapies to manage aging and related diseases.
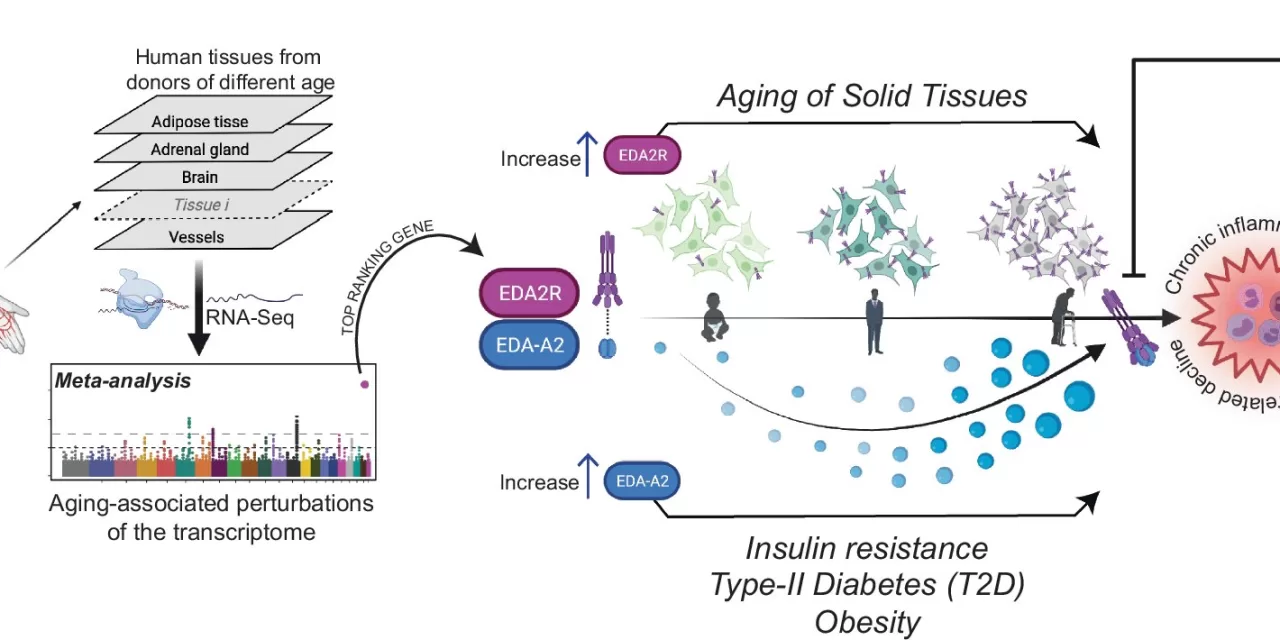
A study published in Nature Communications, led by Dr. Ildus Akhmetov at Liverpool John Moores University, revealed that the Ectodysplasin A2 Receptor (EDA2R) is strongly correlated with aging across various human tissues and organs.
Age-related diseases are often associated with chronic, low-grade inflammation, contributing to conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, neurodegeneration, and sarcopenia. The research team analyzed data from the Genotype-Tissue Expression database and found a consistent link between EDA2R expression and age.
“These findings suggest that the EDA2R/EDA-A2 axis may play a pivotal role in mediating age-related inflammatory and degenerative processes across tissues,” said Dr. Akhmetov.
Further validation in rodent models showed that elevated EDA2R expression was associated with transcriptional changes linked to inflammation and vascular dysfunction, both hallmarks of aging.
The researchers also found that EDA2R not only serves as a biomarker of chronic inflammation but also acts as a potential driver of the aging process. In cellular models, EDA2R overexpression triggered inflammatory signaling and disrupted muscle health pathways, mimicking sarcopenia. Conversely, EDA2R inhibition mitigated these detrimental effects.
Analyzing blood samples from over 5,228 individuals, the team found a strong correlation between EDA2R expression and systemic inflammation, as indicated by elevated C-reactive protein levels.
“Targeting EDA2R could open new therapeutic avenues for managing aging-related conditions, including sarcopenia, cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and metabolic disorders,” Dr. Akhmetov stated.
The study also suggests that lifestyle interventions and certain medications may influence EDA2R levels. “The literature and our preliminary data indicate that calorie restriction, physical activity, the dietary supplement ginkgo, and the widely prescribed glucose-regulating medication metformin can reduce EDA2R levels in animal models and human subjects,” Dr. Akhmetov added.
Future research will focus on developing interventions to modulate EDA2R signaling and reduce the impact of aging.
Disclaimer: This news article is based on information available at the time of publication and reflects the findings of a specific study. Aging research is ongoing, and further studies may provide additional insights or modify current understandings. This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Individuals with concerns about aging or related health conditions should consult with a qualified healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment. The information regarding lifestyle interventions and medications is based on preliminary data and should not be interpreted as a recommendation without consulting a healthcare provider.