The World Health Organization (WHO) recently released new estimates suggesting around 846 million people aged between 15 and 49 live with a genital herpes infection. That’s equivalent to one in every five people from that age group. At least one person each second (42 million people annually) contracts a new genital herpes infection.
What is Genital Herpes?
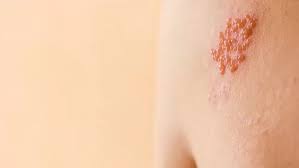
Genital herpes is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the herpes simplex virus, which also causes cold sores.
-
- HSV-1: Primarily associated with oral herpes (cold sores), it can also be transmitted sexually.
- HSV-2: Almost always causes genital herpes infections.
Two Types: There are two types of herpes simplex virus, HSV-1 and HSV-2.
- Transmission:
- Spread through sexual contact, including oral sex.
Can also be transmitted through non-sexual contact, such as sharing utensils or lip balm (with HSV-1).
- Spread through sexual contact, including oral sex.
- Symptoms:
- Initial outbreak often includes painful blisters, ulcers, and peeling skin.
- Many people experience no symptoms or mild symptoms.
- Lifelong Infection: Once contracted, the virus remains in the body, although outbreaks may become less frequent or less severe over time.
Changing Trends:
- Increase in HSV-1 Genital Infections: While HSV-2 remains a significant cause, the prevalence of genital herpes caused by HSV-1 has nearly doubled since 2016.
- Declining HSV-2 Infections: Studies suggest a gradual decline in new HSV-2 genital infections.
Prevention and Management:
- Safe Sex Practices: Consistent condom use during all sexual activities is crucial for reducing the risk of transmission.
- Antiviral Medications: Available to help reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
- Immune Health: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle (sleep, nutrition, stress management) can help strengthen the immune system and reduce the likelihood of outbreaks.
Important Notes:
- Testing: Routine testing for genital herpes is not typically recommended unless there are specific circumstances (pregnancy, severe symptoms).
- Stigma: Addressing the stigma surrounding herpes is crucial for open communication and access to care.
Disclaimer: This information is for general knowledge and does not constitute medical advice. Consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns.
This article provides a concise overview of genital herpes.
Key takeaways:
- Genital herpes is a common and widespread STI.
- Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 can cause genital infections.
- Safe sex practices are essential for prevention.
- Early diagnosis and treatment can improve quality of life.
- Addressing stigma is crucial for effective prevention and management.