December 25, 2024
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) continue to be a global health crisis, with millions affected worldwide, prompting a growing demand for innovative tools that can enable early detection and more effective treatments. Among the most promising solutions are wearable heart sound devices, a groundbreaking technology poised to revolutionize the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cardiovascular conditions. These devices offer continuous, non-invasive monitoring that could dramatically improve patient care by providing real-time insights into heart health.
The urgent need for early intervention in CVDs is underscored by their increasing prevalence and devastating impact on global health. While traditional diagnostic tools such as stethoscopes have been valuable in identifying heart issues, they fall short when it comes to providing continuous monitoring—a critical aspect in managing chronic conditions and preventing heart attacks or strokes.
Wearable technology has emerged as a transformative solution, allowing for persistent heart sound tracking. These devices have the potential to detect early signs of cardiovascular problems and alert patients or doctors to take action before a condition worsens. However, challenges such as achieving the right balance of sensitivity, comfort, and data accuracy still pose barriers to widespread adoption.
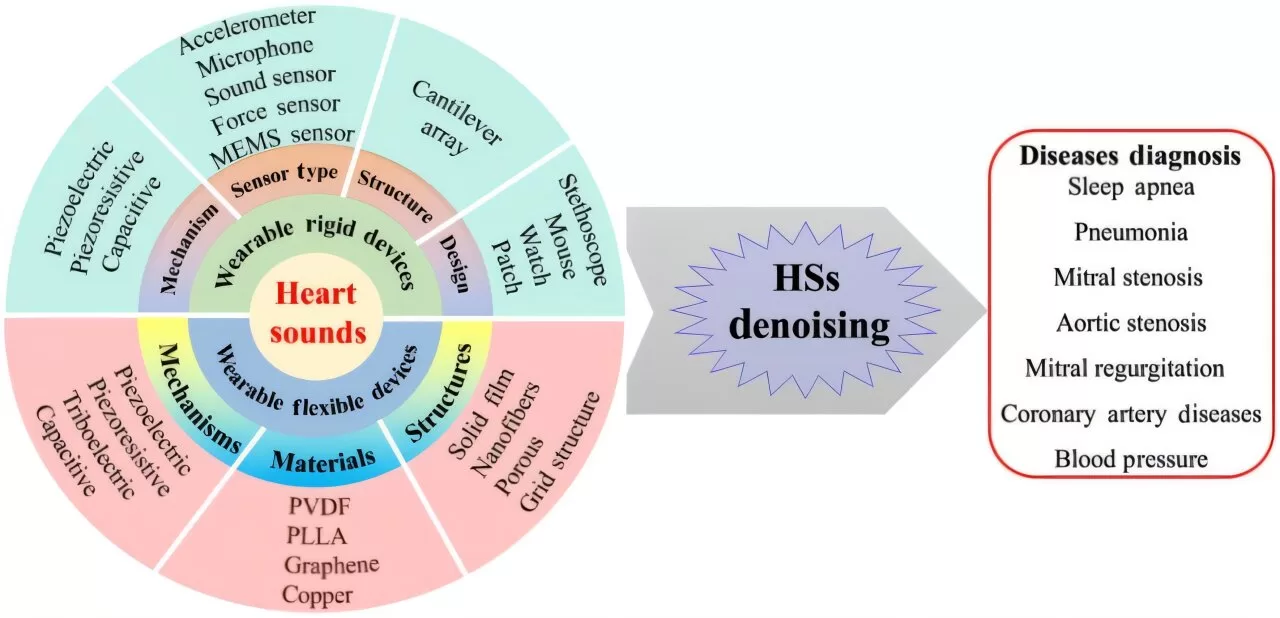
In a recent study, researchers from the City University of Hong Kong explored the latest advancements in wearable heart sound sensors, publishing their findings in SmartMat. The research provides an in-depth look at the sensor types, material innovations, design principles, and denoising techniques that are shaping the future of cardiac health monitoring. By overcoming the challenges of traditional stethoscopes, these wearable devices can provide more accurate and real-time data, improving outcomes for patients worldwide.
Key developments highlighted in the study include the creation of mechanoacoustic sensors with soft, flexible designs that prioritize comfort without compromising on sensitivity and specificity. These sensors are capable of monitoring heart sounds with greater precision, making them an essential tool in continuous cardiac activity tracking.
The researchers also emphasize the importance of advanced materials and optimized design principles in overcoming obstacles in heart sound monitoring. Denoising techniques are crucial to filtering out environmental noise and improving the accuracy of low-frequency cardiac sounds, which are often distorted by external factors. By refining these aspects, wearable heart sound devices can offer a more reliable and comprehensive picture of heart health.
In addition to these technical innovations, the study explores the clinical applications of wearable heart sound devices. Researchers envision a future where personalized health care and remote monitoring are seamlessly integrated into cardiovascular disease management. This approach would enable doctors to access real-time data, facilitating more precise diagnoses and timely interventions that could significantly enhance patient outcomes.
Dr. Bee Luan Khoo, Associate Professor at the City University of Hong Kong and one of the authors of the study, comments: “Our work on wearable heart sound devices marks a significant step forward in the early detection and monitoring of cardiovascular diseases. These devices have the potential to provide more accurate, real-time cardiac health data, revolutionizing the way we manage and understand heart health.”
The potential impact of wearable heart sound devices is profound. Not only could they redefine the practice of remote patient monitoring, but they could also empower patients to take a more active role in managing their heart health. With continuous monitoring, patients could detect irregularities early, seek intervention sooner, and potentially reduce mortality rates linked to cardiovascular diseases.
These advancements also have the potential to reduce the strain on healthcare systems by offering doctors a wealth of continuous data to inform more personalized and efficient treatment plans. As wearable technology continues to evolve, the integration of these devices into everyday healthcare could significantly shift the landscape of cardiac care, making it more proactive and accessible.
In conclusion, the promise of wearable heart sound devices represents a hopeful leap toward a healthier future. With their ability to continuously monitor heart health and provide real-time insights, these devices offer an innovative solution to one of the world’s most pressing health challenges—cardiovascular disease.
For further reading:
Rafi u Shan Ahmad et al., Advancements in wearable heart sounds devices for the monitoring of cardiovascular diseases, SmartMat (2024). DOI: 10.1002/smm2.1311