December 18, 2024
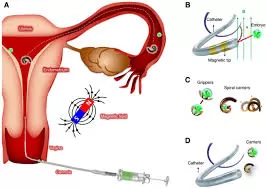
Infertility, a condition affecting an estimated 186 million people worldwide, often stems from various factors, including fallopian tube obstruction—a contributor to 11%-67% of female infertility cases. Now, an innovative breakthrough from the SIAT Magnetic Soft Microrobots Lab offers a cutting-edge solution to this challenge: a magnetically driven robotic microscrew designed to clear blockages in the fallopian tubes.
Published in AIP Advances by AIP Publishing, the study showcases how these tiny yet mighty robots could revolutionize infertility treatment.
A Less Invasive Alternative
Current surgical treatments for tubal obstructions often rely on catheters and guidewires, which can be invasive and uncomfortable for patients. The new microrobot, crafted from a photosensitive resin coated with a thin layer of iron for magnetic properties, offers a promising alternative.
“This new technology provides a potentially less invasive solution for clearing tubal obstructions,” explained Haifeng Xu, one of the researchers.
Using an external magnetic field, the microrobot rotates, generating a motion that allows it to navigate through a simulated fallopian tube—a glass channel in laboratory tests. Impressively, the microrobot successfully cleared cell clusters that mimicked typical blockages in the female reproductive system.
Designing the Future of Infertility Treatment
The microrobot’s innovative design is key to its effectiveness. It features:
- A screw-shaped body with a helical structure for propulsion.
- A cylindrical central tube for structural support.
- A disk-shaped tail for motion stability.
As the screw rotates, it creates a vortex field that fragments and propels debris away from the blockage. This mechanism ensures precise and efficient clearance without damaging the delicate structures of the fallopian tube.
Promising Results and Future Plans
Tests have demonstrated the microrobot’s efficiency in clearing blockages, making it a potential game-changer in infertility treatments. Looking ahead, the research team is focused on refining the technology further.
Plans include:
- Miniaturizing the microrobot for enhanced precision.
- Testing in isolated organ models to simulate real-world conditions.
- Incorporating in vivo imaging systems to track the robot’s movements in real time.
- Developing automatic control systems for surgical applications beyond infertility treatments.
“The ultimate goal is to provide a more effective, minimally invasive solution for patients suffering from infertility,” Xu emphasized.
Beyond Infertility
The potential applications of this microrobot extend far beyond reproductive health. Researchers envision its use in various surgical procedures, offering a glimpse into a future where magnetic microrobots could transform modern medicine.
As these tiny robots continue to evolve, they may soon bring hope to millions of individuals facing infertility, proving that sometimes the smallest solutions can have the most profound impact.