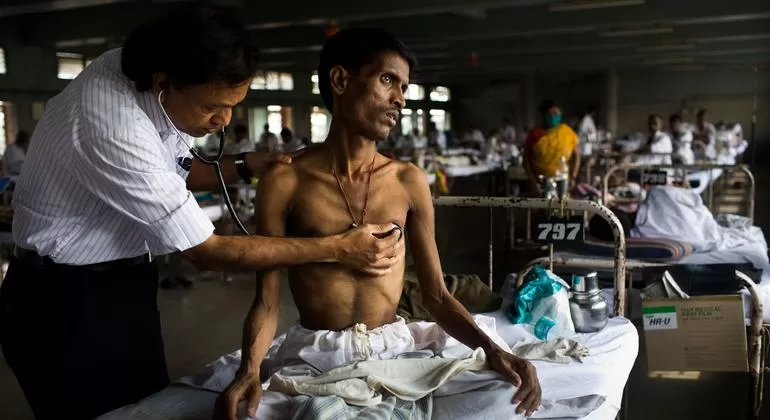
New Delhi: Tuberculosis (TB) patients in India are bearing a heavy financial burden due to lost productivity and hospitalisation, according to a recent study conducted by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Despite the availability of free diagnosis and treatment under the National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP), many patients continue to experience significant economic strain, the study revealed.
Led by researchers from the ICMR-National Institute of Epidemiology (ICMR-NIE) in Chennai, the study highlights the substantial social and economic challenges posed by TB to Indian households. “Nearly half of TB patients, particularly those from poorer economic backgrounds, face catastrophic costs,” said Dr. Kathiresan Jeyashree, the lead scientist of the study.
The findings, published in the journal Global Health Research and Policy, assessed the financial burden on 1,407 TB patients by examining direct medical costs, non-medical expenses, and lost productivity. Catastrophic costs were defined as expenses exceeding 20% of a household’s annual income.
Key Findings:
- Demographics: The mean age of the participants was 40.8 years, with 61.5% being male. Over half (55.9%) were economically active.
- Financial Burden: On average, direct costs accounted for 34% of total expenses. Patients younger than 60, without health insurance, and those requiring hospitalisation incurred higher costs.
- Hospitalisation and Drug-Resistant TB: Among the participants, 18.3% had been hospitalised, and 2.4% were diagnosed with drug-resistant TB. Hospitalised patients, as well as those seeking treatment from private-sector providers, were particularly prone to catastrophic expenses.
- Catastrophic Costs: Approximately 45% of TB patients experienced expenses classified as catastrophic.
Policy Implications:
The study underscores the need for enhanced measures to alleviate the economic burden on TB patients. Recommendations include:
- Early Notification: Encouraging timely diagnosis to reduce prolonged treatment costs.
- Expanded Health Insurance Coverage: Integrating TB care into broader health insurance schemes.
- Addressing Social Determinants: Implementing strategies targeting the underlying social factors contributing to TB.
“Addressing the financial challenges associated with TB is critical to achieving India’s goal of eliminating the disease by 2025,” Dr. Jeyashree emphasized. “Strategies to expand healthcare coverage and reduce out-of-pocket expenses are essential to prevent financial catastrophes among affected households.”
With TB continuing to exert a significant toll on patients and their families, the study calls for urgent action to improve access to affordable care and address the socioeconomic factors driving the disease.