Recent Study Unveils Potential Benefits of Fermented Lingonberry Juice for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
In a groundbreaking study published in the journal Nutrients, scientists from Finland and Sweden have explored the remarkable benefits of fermented lingonberry juice in alleviating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This research highlights the anti-inflammatory, anti-proteolytic, antimicrobial, and prebiotic properties of this unique beverage, shedding light on its potential to support gut health and manage IBD symptoms.
Understanding the Gut Microbiome’s Role
The link between gut health and overall well-being has gained significant attention, with recent research focusing on the impact of oral and gut microbiomes on gastrointestinal inflammation. The study emphasizes how oral microbes can influence gut health, potentially exacerbating conditions like IBD through pathogen transmission. Dysbiosis, or microbial imbalance, can compromise the intestinal barrier and contribute to various metabolic and autoimmune disorders, including IBD.
IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by excessive inflammation of the intestinal mucosa. Factors such as genetic predisposition, smoking, diet, and pathogens are known triggers. Oral symptoms often accompany IBD, underscoring the importance of oral health in managing the disease.
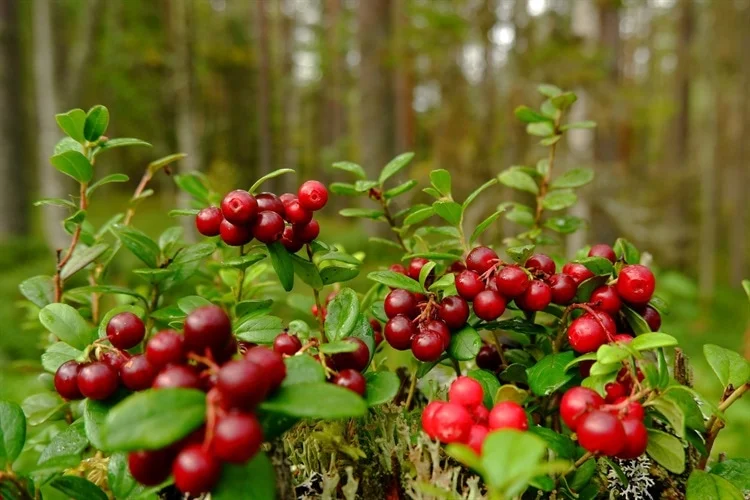
Lingonberries: A Potential Game Changer
Lingonberries (Vaccinium vitis-idaea), native to the northern hemisphere, have long been recognized for their health benefits. The study identifies bioactive compounds in lingonberries, such as flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes like resveratrol, known for their anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. These compounds can influence the gut microbiome, promoting beneficial bacteria while inhibiting pathogenic strains.
Fermented lingonberry juice, in particular, has shown promise in reducing oral inflammation and improving oral health. Clinical trials of a natural mouth rinse based on fermented lingonberry juice demonstrated significant benefits, including reduced periodontal inflammation, decreased gum bleeding, and improved oral plaque control.
Implications for IBD Management
The study’s findings suggest that fermented lingonberry juice could extend its benefits beyond oral health to the gut. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and reducing inflammation, this juice may offer a supportive role in managing IBD. Fermentation enhances the bioavailability of phenolic compounds, making them more effective in lowering proteolytic inflammation and inhibiting opportunistic pathogens.
Researchers propose that oral health interventions, such as incorporating fermented lingonberry juice, might indirectly benefit gut health by modulating the oral microbiome. However, they call for further research and human clinical trials to fully understand the juice’s impact on gastrointestinal inflammation and IBD symptoms.
Conclusion
The study provides a promising outlook on the use of fermented lingonberry juice as a potential adjunctive treatment for IBD. By leveraging its anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and prebiotic properties, fermented lingonberry juice could play a role in managing gut health and alleviating IBD symptoms. Future research will be crucial in validating these findings and exploring the full potential of this natural remedy.
For more details, you can access the study here: Nutrients 16, DOI: 10.3390/nu16172896.