Effective Disease Management: Early Detection, Treatment, and Rapid Response Set Up by the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare
In a recent push to combat malaria, the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare has rolled out an array of comprehensive measures aimed at bolstering malaria prevention and control across the nation. This initiative underscores the government’s commitment to eradicating malaria by focusing on early detection, effective treatment, and rapid response mechanisms.
Disease Management Strategy
Central to the new measures is an enhanced disease management strategy. This involves:
- Early Case Detection: Implementing active, passive, and sentinel surveillance to identify cases promptly.
- Effective Treatment: Ensuring complete and effective treatment for all detected cases.
- Strengthening Referral Services: Enhancing the referral system to ensure patients receive timely and appropriate care.
- Epidemic Preparedness: Boosting preparedness for potential outbreaks.
- Rapid Response: Establishing quick response teams to address outbreaks and control the spread of malaria swiftly.
Integrated Vector Management
A robust integrated vector management strategy has been introduced, focusing on multiple fronts to reduce mosquito populations and prevent malaria transmission:
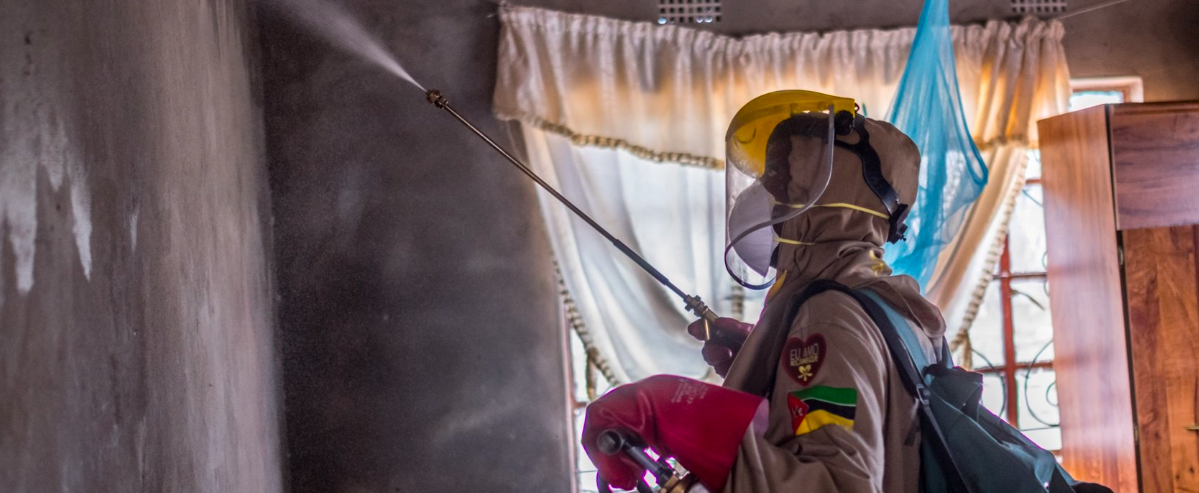
- Indoor Residual Spraying (IRS): Targeted spraying in high-risk areas to kill mosquitoes that come in contact with treated surfaces.
- Long Lasting Insecticidal Nets (LLINs): Distribution of insecticide-treated nets in high malaria endemic regions to protect individuals from mosquito bites.
- Larvivorous Fish: Utilization of fish that feed on mosquito larvae in water bodies to control mosquito populations naturally.
- Anti-Larval Measures: Implementation of bio-larvicides and minor environmental engineering projects in urban areas to eliminate mosquito breeding sites.
Supportive Interventions
The government’s approach is not limited to direct medical interventions. It also includes supportive measures aimed at sustaining the effectiveness of the malaria prevention efforts:
- Behaviour Change Communication (BCC): Educating communities about malaria prevention practices and encouraging behavior that reduces the risk of malaria.
- Inter-Sectoral Convergence: Coordinating efforts across different sectors to ensure a holistic approach to malaria control.
- Capacity Building: Training and developing human resources to improve the efficiency and reach of malaria prevention programs.
National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) 2016-2030
As part of its long-term vision, the government has launched the National Framework for Malaria Elimination (NFME) 2016-2030. This ambitious plan aims to achieve zero indigenous cases of malaria by 2027 and sustain elimination by 2030. The framework outlines strategic interventions, resource allocation, and monitoring mechanisms to ensure the systematic and sustained eradication of malaria.
In a written reply in the Lok Sabha, the Minister of State in the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Shri Prataprao Jadhav, highlighted these initiatives, emphasizing the technical and financial support provided to states and Union Territories (UTs) for nationwide malaria prevention. The collaborative effort between the central government, states, UTs, and various stakeholders marks a significant step forward in the fight against malaria, with the ultimate goal of making India malaria-free.
These measures reflect the government’s proactive stance in tackling malaria and demonstrate a comprehensive approach to public health management, which, if successful, could serve as a model for other countries grappling with similar challenges.