The rise of computerized trading and fintech platforms has democratized stock market investing, leading to a significant increase in global stock market participation. In China, this trend is particularly pronounced, with the number of stock investors soaring from 29.3 million in 2000 to a staggering 322.6 million in 2022. However, this surge in investment activity also brings potential challenges, particularly regarding the mental and physical health of investors.
Researchers from the National University of Singapore, Jinan University, Peking University, and Sun Yat-sen University recently conducted a study to explore the correlation between stock market fluctuations and stress-related emergency room visits in China. Published in Nature Mental Health, the study revealed a marked increase in emergency room visits for mental health issues during periods of stock market volatility.
Significant Findings
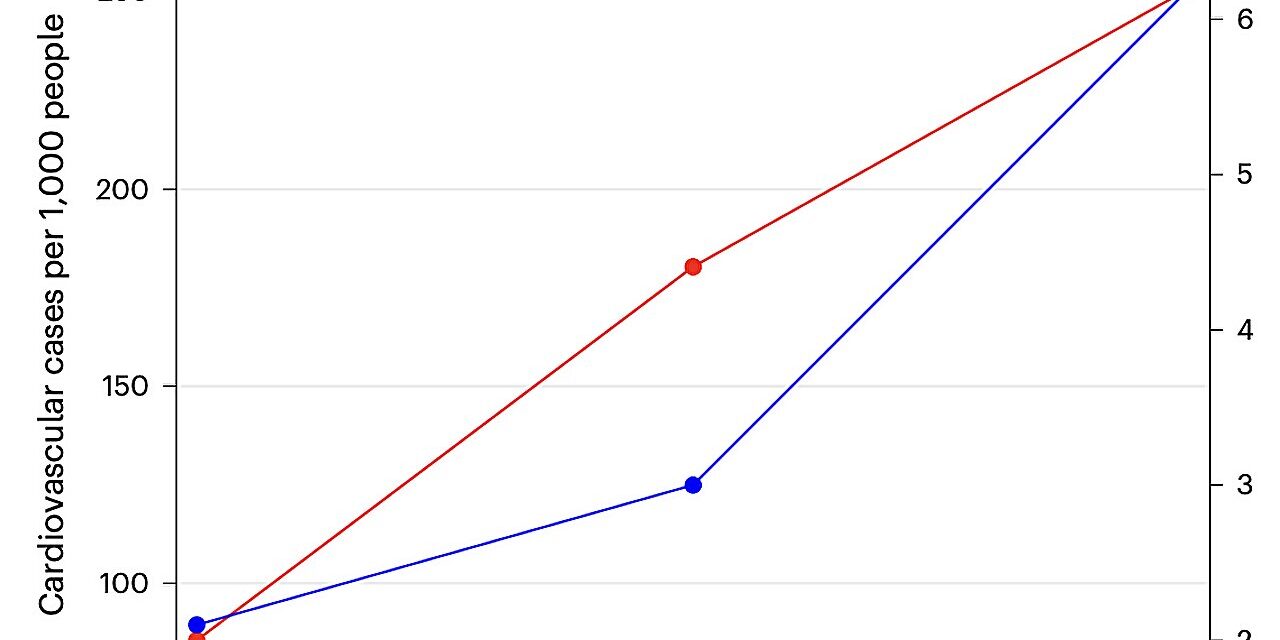
The research team focused on data from Beijing’s largest hospitals, spanning three years from 2009 to 2012. They analyzed emergency room visits for stress-related conditions alongside stock market trends. The study found that a one percentage point decrease in daily market returns on the Growth Enterprises Index correlated with a 0.7% increase in cases of cardiovascular diseases and a 2.5% increase in mental disorders on the same day.
Conversely, a one percentage point increase in daily market returns was associated with a 3.3% increase in cases of alcohol abuse on the day of the market change. These findings indicate that stock market volatility has immediate and tangible effects on investors’ physical and mental health.
Broader Implications
Sumit Agarwal, Siyu Chen, and their colleagues highlighted the non-linear, instantaneous nature of these health effects, noting that older individuals and males are particularly vulnerable. Interestingly, diseases less related to psychological stress, such as infections and parasitic diseases, did not show a significant correlation with market fluctuations.
The study also suggested that a ten percentage point decrease in daily market returns could lead to an estimated RMB 35 million increase in national medical expenses related to emergency room services. This highlights the potential economic impact of stock market volatility on the healthcare system.
Future Research Directions
Given the age of the data used in the study, the researchers emphasized the need for further research using newer medical and financial data. They suggested that the digital medical data collected during the COVID-19 pandemic could provide valuable insights, as many individuals accessed online medical services during this period.
The findings from this study underscore the importance of understanding the broader implications of stock market fluctuations, particularly their impact on public health. As the number of investors continues to grow, further research in this area could inform policies and interventions aimed at mitigating the adverse health effects of financial market volatility.
For more information, see the full study: Sumit Agarwal et al, “Associations between stock market fluctuations and stress-related emergency room visits in China,” Nature Mental Health (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44220-024-00267-5.