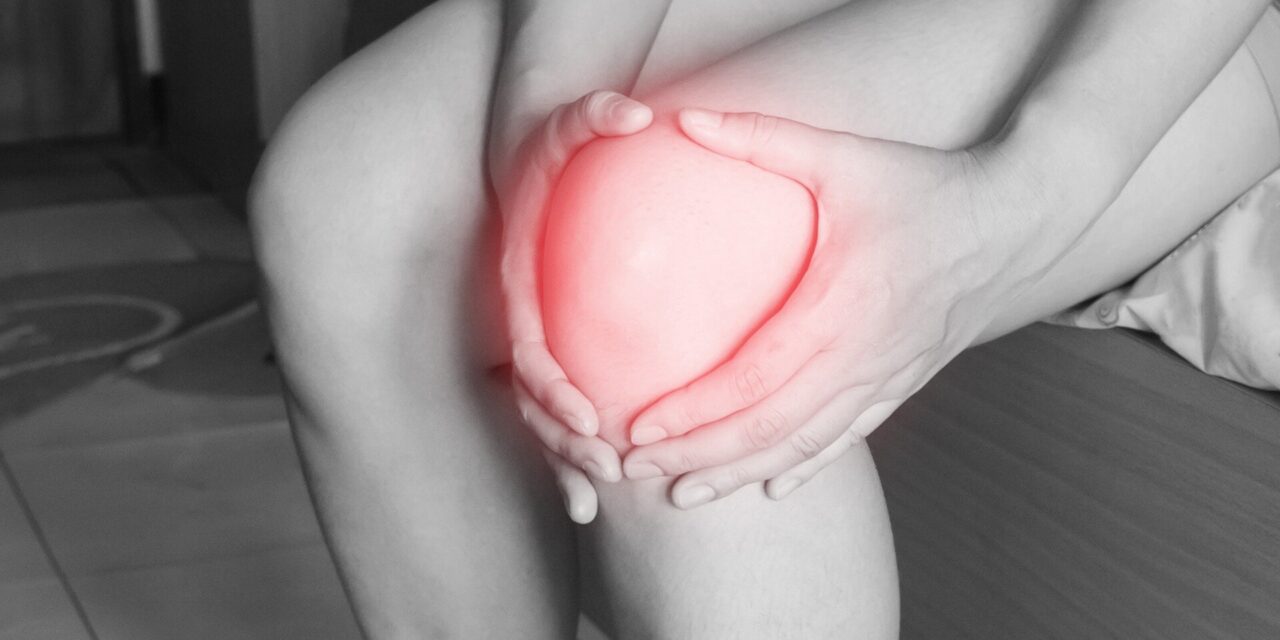
In a significant advisory, a top neurologist has recommended that individuals suffering from knee osteoarthritis should avoid physical activities such as walking, running, or playing sports. This advice comes in light of new research findings suggesting that such activities may exacerbate the condition.
Knee osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease, is characterized by chronic pain and limited joint movement due to the progressive loss of articular cartilage. While exercise is generally known to improve health, its impact on those with knee osteoarthritis appears to be detrimental, according to Sudhir Kumar of Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals, Hyderabad. Citing a recent study published in the JAMA Network Open, Kumar advised patients to avoid weight-bearing physical activities.
“People with knee osteoarthritis should focus on non-weight bearing activities, such as cycling or swimming, as these are not linked with the incidence of knee osteoarthritis,” Kumar stated.
The study in question, conducted by researchers from the University Medical Center Rotterdam in the Netherlands, included 5,003 participants, of whom 2,804 were women. The findings indicated that weight-bearing activities were not associated with knee osteoarthritis in individuals with intermediate or high lower-limb muscle mass index (LMI).
“Individuals with low lower limb muscle mass or strength should prefer non-weight-bearing physical activities,” Kumar emphasized. He also highlighted the importance of lower limb muscle strengthening exercises, particularly for the quadriceps, for those who engage in weight-bearing activities.
“People with good lower limb muscle mass and strength can safely continue with weight-bearing activities without the fear of knee pain or developing knee osteoarthritis,” Kumar concluded.
This advisory underscores the need for personalized exercise regimens tailored to individual muscle mass and strength, ensuring that patients with knee osteoarthritis can maintain their health without exacerbating their condition.