In a groundbreaking study published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, researchers at the University of Missouri have uncovered promising evidence that the juice from red cabbage may hold therapeutic benefits for individuals suffering from inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Led by Santayana Rachagani, an associate professor in Mizzou’s Department of Veterinary Medicine and Surgery, the research team delved into the pharmaceutical effects of natural foods, known as nutraceuticals, in modulating gut microbiota and alleviating inflammation-associated conditions such as IBD. Their findings offer hope to the estimated 3 million Americans afflicted by IBD, offering a potential alternative or complementary treatment approach.
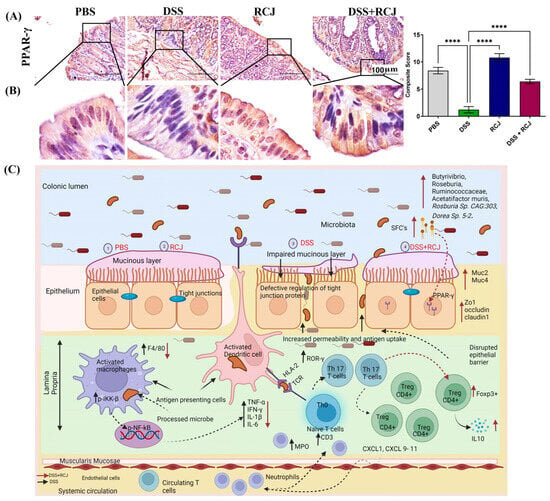
The study, titled “Red Cabbage Juice-Mediated Gut Microbiota Modulation Improves Intestinal Epithelial Homeostasis and Ameliorates Colitis,” sheds light on the diverse array of bioactive compounds found in red cabbage juice, which have been shown to improve gut health and alleviate symptoms of IBD in mice.
According to Rachagani, red cabbage juice exhibits the ability to alter the composition of gut microbiota by increasing the abundance of beneficial bacteria, leading to the production of short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites that contribute to reduced inflammation. These changes are associated with improved gut barrier function, enhanced colon repair, and anti-oxidative effects, ultimately mitigating intestinal damage and inflammation.
Nagabhishek Sirpu Natesh, a post-doctoral fellow involved in the project, emphasized that red cabbage juice treatment increased levels of beneficial gut bacteria, triggering anti-inflammatory responses in the colons of mice. Additionally, it boosted regulatory T cells, promoting an immune balance that further reduced colonic inflammation.
The study’s findings provide valuable insights into potential therapeutic avenues for IBD, particularly for patients who may experience diminishing effectiveness with current pharmacological treatments. While monoclonal antibodies are the primary approach for addressing inflammation in IBD, many patients find that their efficacy wanes over time. Rachagani and his team suggest that red cabbage juice may offer a complementary or alternative solution by targeting the molecular mechanisms underlying IBD.
Beyond its ability to modulate gut microbiota and activate anti-inflammatory pathways, red cabbage juice is also rich in dietary fiber, further enhancing its potential for promoting gut health.
“These findings underscore the potential of red cabbage juice as a valuable therapeutic agent for IBD and related inflammatory disorders,” Rachagani stated. “By harnessing the bioactive compounds found in natural foods like red cabbage, we may unlock new treatment options and improve outcomes for individuals living with IBD.”
As researchers continue to explore the therapeutic potential of nutraceuticals, red cabbage juice stands out as a promising candidate for alleviating the burden of IBD and enhancing the quality of life for millions of affected individuals worldwide.