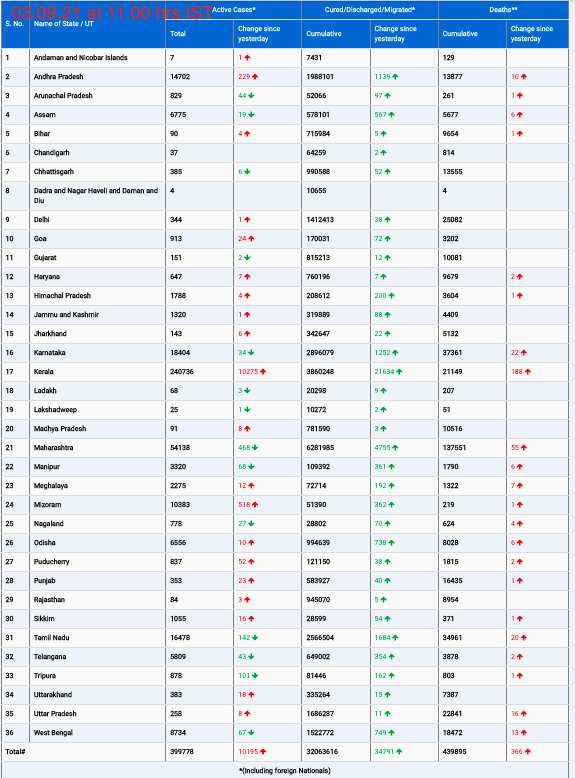
A concerning trend has emerged in recent years as rates of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) among people aged 55 and older have risen sharply, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The latest STI surveillance report from the agency reveals a troubling increase in cases of gonorrhea, chlamydia, and syphilis among this demographic over the past decade.
Between 2012 and 2022, the number of gonorrhea cases among individuals aged 55 and older surged approximately fivefold, while cases of chlamydia tripled, and syphilis cases increased by roughly seven times. The overall spike in STI diagnoses, particularly in syphilis, has been significant, with rates soaring nearly 80% between 2018 and 2022.
While STIs have long been associated with younger age groups, the upward trend among older adults serves as a stark reminder that sexual health is important at any age. Dr. Jason Zucker, an infectious disease expert at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, emphasized the need to recognize that STIs can affect anyone who is sexually active, regardless of age.
Several factors contribute to the rise in STIs among older adults, experts say. Improved health and longevity have led to sustained sexual activity later in life, while medications for conditions like menopause-related vaginal dryness and erectile dysfunction have facilitated continued sexual activity. However, compared to younger generations, older adults often lack education about STI prevention and testing, leaving them vulnerable to infection.
Physiological changes associated with aging, such as thinning vaginal walls and decreased cervical mucus, can also increase susceptibility to STIs among older women.
To address the rising rates of STIs among older adults, experts stress the importance of comprehensive sexual health education and services tailored to this demographic. Dr. Hugh Taylor, chair of OB/GYN at Yale School of Medicine, highlighted the need for healthcare providers to regularly assess sexual health needs and offer preventive services to older patients.
Effective strategies to reduce STI rates among older adults include increasing access to condoms and lubricants, providing behavioral counseling, offering vaccinations, and implementing routine screenings. Education campaigns targeting older adults and healthcare providers are also crucial to raise awareness about STI prevention and testing.
Ultimately, proactive communication between older patients and healthcare providers about sexual health is essential in promoting safe and healthy sexual practices.
As rates of STIs continue to climb among older adults, concerted efforts are needed to address the unique challenges and vulnerabilities faced by this demographic, ensuring that comprehensive sexual health services are accessible to all individuals, regardless of age.