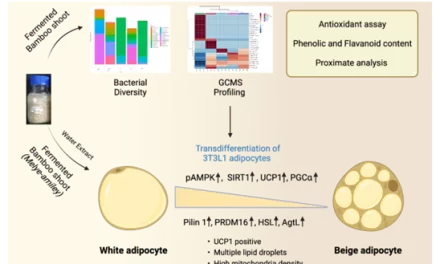
A recent analysis has unveiled the protective benefits of leisure time physical activity against stroke, challenging the notion that intense exercise is necessary for risk reduction. The study, encompassing over 750,000 adults across 15 research works, highlights the potential of even minimal levels of activity to significantly mitigate stroke risk, irrespective of age or sex.
Contrary to previous assumptions that moderate to high levels of physical activity are required for stroke prevention, the analysis demonstrates that engaging in activities falling below current recommended guidelines can still offer substantial protective effects.
The study, published in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, underscores the importance of encouraging physical activity at all levels. Lead researcher Dr. [Researcher’s Name] notes, “According to our results, all levels of leisure time physical activity can be beneficial for stroke prevention, including levels currently regarded as low or insufficient. People should be encouraged to be physically active even at the lowest levels.”
The analysis revealed that compared to those with no leisure time physical activity, individuals engaging in the highest “ideal” level experienced a 29% reduction in stroke risk. Intriguingly, even “below target” levels of activity were associated with an 18% risk reduction. This trend persisted across various intensities of activity, suggesting that even minimal amounts of physical activity could contribute significantly to stroke prevention over the long term.
Moreover, the benefits of moderate activity remained consistent across different demographic groups, indicating that age and sex did not diminish the protective effects of leisure time physical activity.
Leisure time physical activity encompasses a wide range of activities, from walking and swimming to playing sports and practicing yoga. Dr. [Researcher’s Name] emphasizes the importance of selecting activities that align with individual interests, capabilities, and lifestyle, as enjoyment and sustainability are key factors in maintaining a physically active lifestyle.
In addition to stroke prevention, engaging in leisure time physical activity offers numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular health, enhanced mood, weight management, and increased muscle and bone strength. It also provides valuable opportunities for social interaction and outdoor exposure, further enhancing its mental health benefits.
The study’s findings provide compelling evidence that even small amounts of physical activity during leisure time can have significant long-term health benefits, underscoring the importance of incorporating movement into daily life for overall well-being.