February 3, 2025 | International Journal of Molecular Sciences
A recent study led by PD Dr. Stefan Schülke, head of the Research Allergology Division at the Paul-Ehrlich-Institut, has unveiled promising results regarding the immunomodulatory properties of β-glucans, natural sugar compounds found in bacteria, fungi, and grains. Published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the research suggests that β-glucans could play a crucial role as adjuvants in allergy treatment by modulating the immune system.
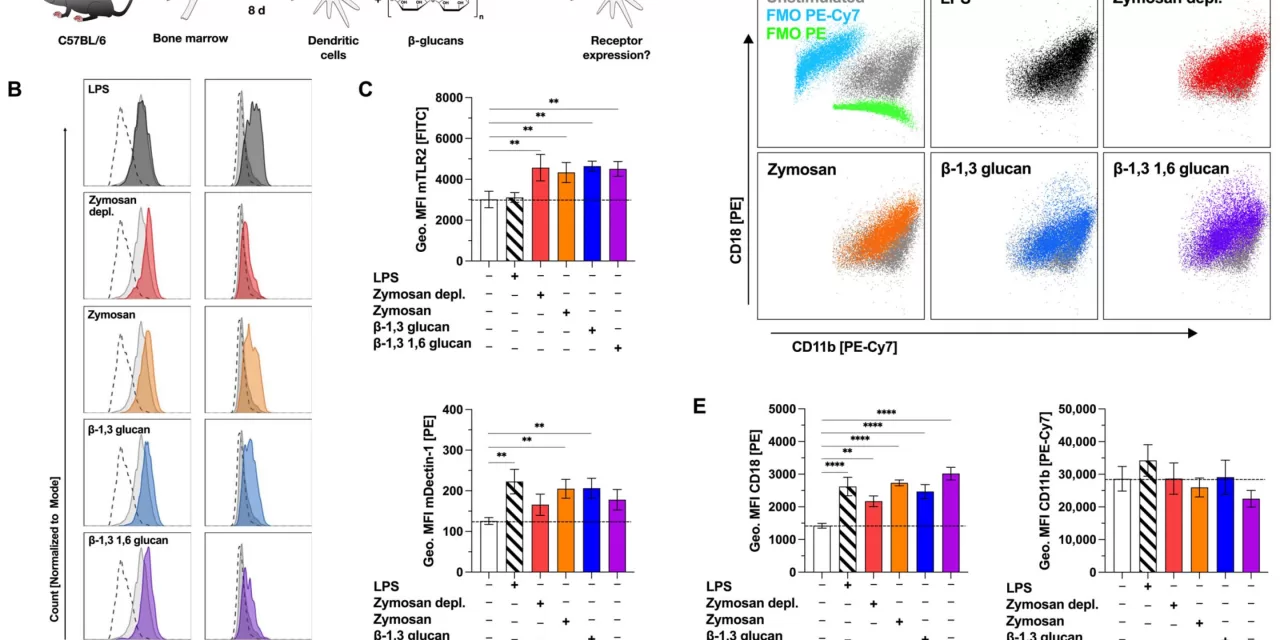
β-glucans have long been known for their ability to influence immune responses, but their potential to suppress allergic reactions is now being explored in greater depth. The research team investigated the effects of six different β-glucans, including zymosan and β-1,3 glucan, on immune cells and inflammatory processes. The findings indicate that these substances activate specific immune receptors and can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory markers, showing potential for suppressing allergy-related immune responses.
Adjuvants, substances that enhance the body’s immune response, have traditionally been used in vaccines to strengthen immunity. In the context of allergies, they could help reduce allergic reactions and promote tolerance to allergens through allergen-specific immunotherapy. This form of treatment seeks to target and modulate immune responses, specifically those mediated by Th2 cells, to decrease sensitivity to specific allergens over time.
In this study, β-glucans were shown to activate dendritic cells, immune cells that play a key role in the body’s response to allergens. The β-glucans tested were found to influence both cytokine secretion and cell metabolism, enhancing the immune system’s ability to respond to allergens. Notably, zymosan and β-1,3 glucan reduced the secretion of inflammatory substances and demonstrated a promising ability to suppress allergy-related immune responses in experimental settings.
In a more detailed analysis, the study revealed that β-glucans such as zymosan and β-1,3 glucan were able to regulate key surface markers on dendritic cells, further suggesting their potential for immune modulation. The research team also found that these compounds could reduce the secretion of IL-5 and interferon gamma (IFNγ), two key cytokines involved in allergic reactions.
The results from this study indicate that β-glucans could become an essential component in the future of allergy treatment, offering a targeted approach to controlling immune responses and preventing allergic reactions. As researchers continue to explore these possibilities, β-glucans may open new avenues for therapeutic strategies in allergy management.
Disclaimer: This article is based on preliminary findings and further research is necessary to fully understand the potential of β-glucans in allergy treatment. The results of this study are not conclusive and should not be considered as medical advice.